Precision
In 3D printing, precision and accuracy are just as important as visual quality. Even if your print looks perfect, it’s of little use if it doesn’t meet the exact dimensional requirements. That’s where the Precision settings in Orca Slicer comes in that helps you tune your every detail for accurate, high-quality results.
These settings allow you to control the geometric accuracy of your prints by reducing distortions, eliminating artifacts, and correcting minor structural deformities. Whether you’re printing mechanical parts that require a perfect fit or aesthetic models that demand flawless surfaces, Orca Slicer’s Precision tools give you full control over the final output.
Let’s explore how you can configure these Precision settings to improve print accuracy, enhance detail, and ensure every model comes out exactly as designed.
How to Configure Precision Settings in Orca Slicer
In Orca Slicer, the Precision Settings under the Quality tab let you control how accurately your 3D model is sliced and printed. These options help eliminate tiny gaps, improve curved surfaces, and reduce unnecessary G-code complexity, all contributing to smoother, high-quality prints.
Below, we’ll go through each precision parameter, explain its purpose, and share optimization tips to help you get the most accurate results possible.
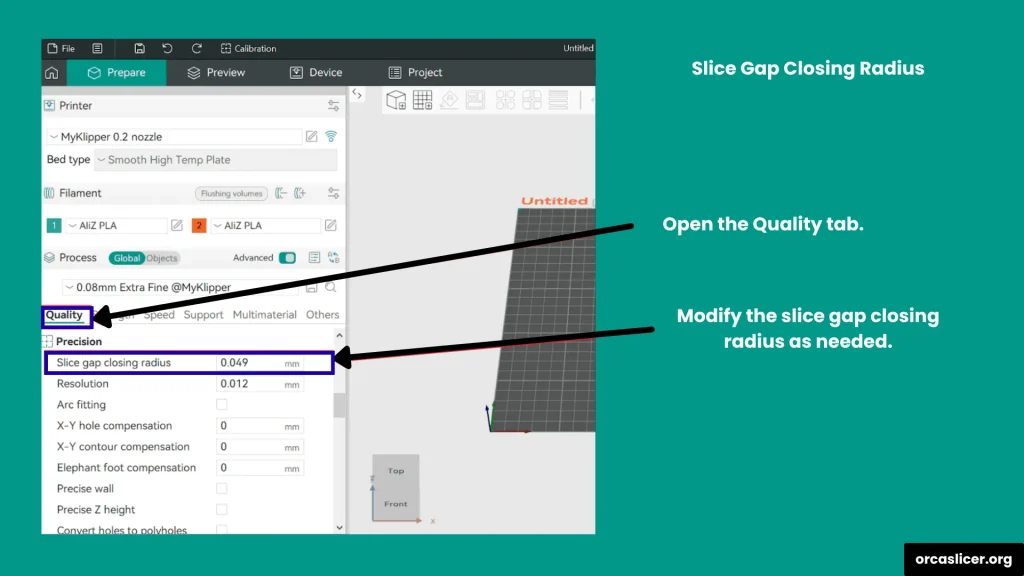
Slice Gap Closing Radius
When printing 3D models, you may sometimes notice tiny gaps between surfaces due to imperfect meshes or slicing limitations. The Slice Gap Closing Radius fixes this by identifying and filling smaller gaps during slicing.
How it works:
- Any crack smaller than 2× the gap closing radius will be automatically filled.
- For instance, if set to 0.01 mm, the printer fills any gap smaller than 0.02 mm.
Optimization Tips:
- Keep this value low (around 0.01 mm) to preserve resolution while sealing small imperfections.
- Higher values may fill large gaps but can reduce print detail and slightly lower the resolution.
This setting is essential for improving print surface integrity and eliminating unwanted holes without distorting fine model details.
Resolution
The Resolution setting defines how finely Orca Slicer interprets the geometry of your 3D model. It simplifies sharp corners and complex edges to generate smoother toolpaths.
- Lower values = Higher resolution. Smaller values produce more accurate shapes but increase slicing time and processing load.
- Higher values = Faster slicing. Ideal for larger models where ultra-fine detail isn’t critical.
Optimization Tips:
- Use lower resolution (0.01–0.05 mm) for detailed parts or mechanical components.
- Use higher resolution (0.1–0.2 mm) for big, simple models to reduce slicing time.
Balancing this setting ensures your prints maintain sharp details where needed while optimizing slicing performance.
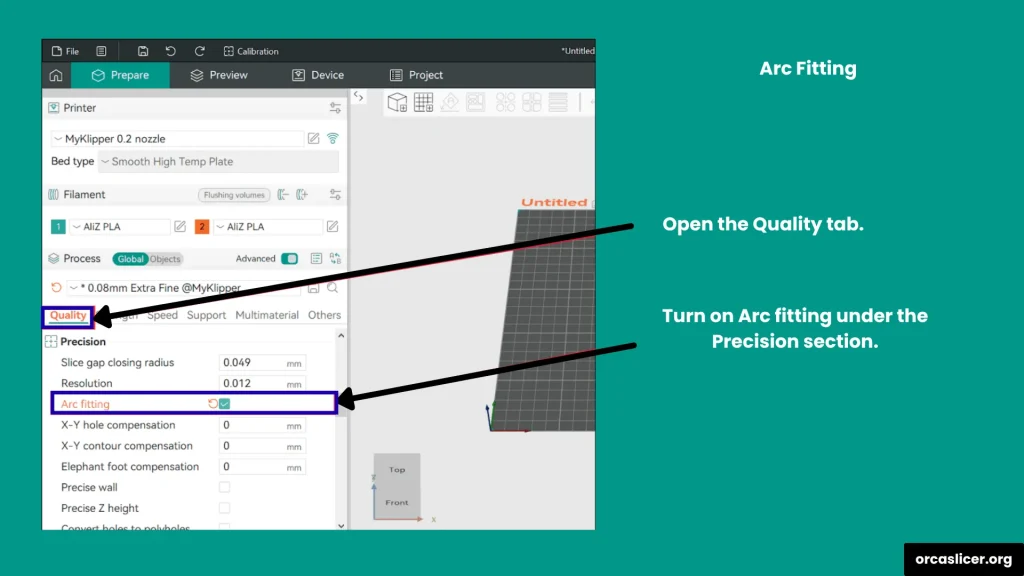
Arc Fitting
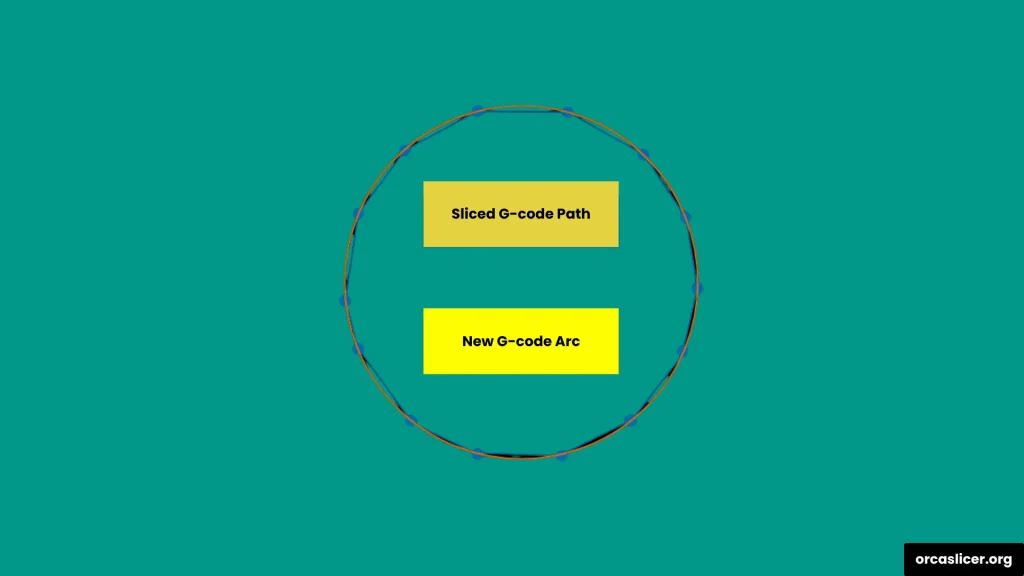
Arc Fitting converts straight-line G-code paths into smooth curved movements, using G2 (clockwise) and G3 (anticlockwise) commands. This reduces the number of commands your printer processes and results in fluid, curved surfaces with better visual quality.
How it works:
- The slicer detects curves in your model and replaces straight line segments with arc motions, creating smoother paths and smaller G-code files.
Advantages
- Produces cleaner circular or curved surfaces.
- Reduces file size by minimizing unnecessary commands.
- Allows faster, more efficient printing with smoother motion control.
Important Points:
- Only use Arc Fitting on printers or firmware that support G2/G3 commands.
- Klipper users: Disable Arc Fitting. Klipper firmware does not support G2/G3, and it will automatically convert arcs back into line segments, lowering precision and wasting processing time.
X-Y Compensation
X-Y Compensation allows you to fine-tune the horizontal dimensions of your model to correct for material expansion or shrinkage. It acts like a tolerance control for the XY plane, adjusting both outer contours and internal holes.
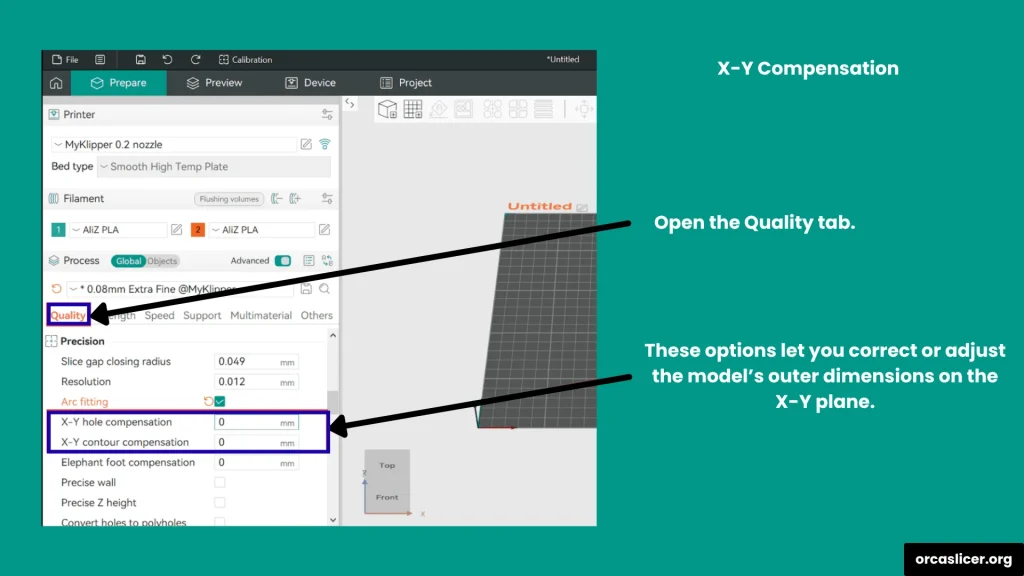
Types:
- X-Y Hole Compensation: Expands or shrinks holes in the XY plane by the chosen value.
- X-Y Contour Compensation: Expands or shrinks the external contour of the model to correct dimensional deviations.
How It Works:
- Positive values (+): Expand the printed part if it shrinks below the expected dimensions.
- Negative values (–): Shrink the printed part if it expands beyond the target size.
Optimization Tips:
- Start with small adjustments, around ±0.02 mm to ±0.05 mm.
- The ideal value depends on factors like filament type, temperature, printer calibration, and ambient conditions.
This compensation ensures your final model matches design specifications precisely, even when the filament behaves unpredictably.
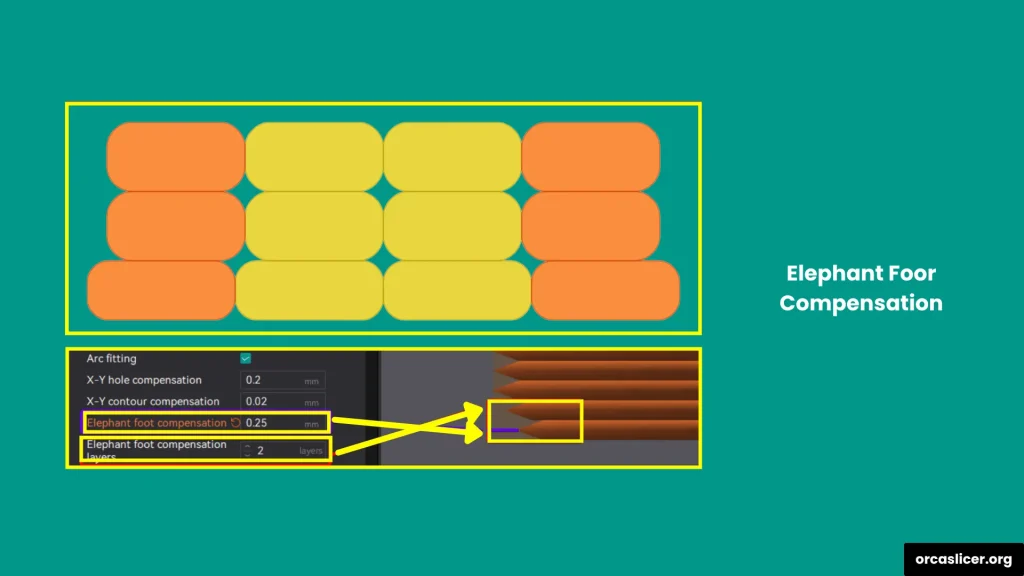
Elephant Foot Compensation
The Elephant Foot Effect occurs when the bottom layers expand outward, creating a wider base than the rest of the print. It’s caused by the heat of the build plate, material pressure, or incorrect bed leveling.
Causes:
- Excessive bed temperature or thermal expansion of the first few layers.
- The weight of upper layers pressing down on the molten base.
- Bed height calibration errors.
Fix:
In Orca Slicer, you can apply Elephant Foot Compensation by assigning a negative value, which reduces the width of the first few layers. For example:
- Setting –0.2 mm prints the bottom layers slightly smaller, balancing expansion and improving accuracy.
This correction ensures a flat, clean base without visible flaring or dimensional inaccuracy.
Precise Wall
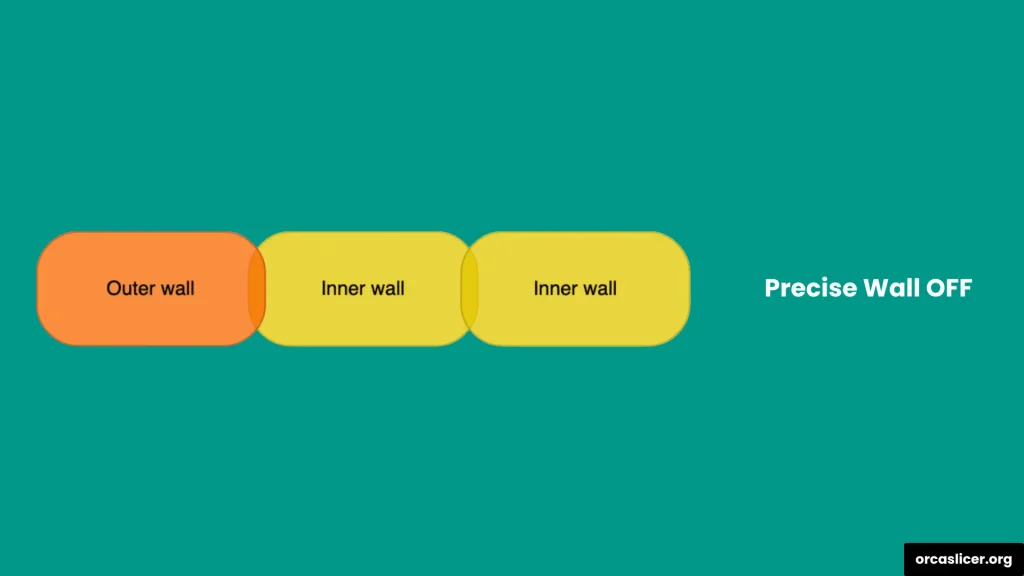
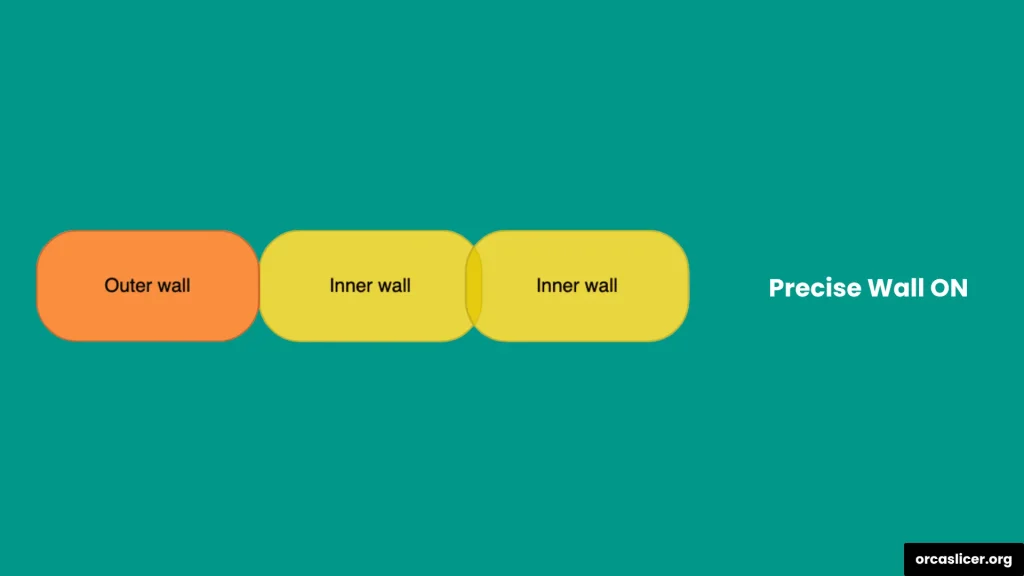
The Precise Wall setting enhances outer wall quality and dimensional precision by managing the spacing between inner and outer perimeters.
Technical Insight:
In slicers like Slic3r, Orca Slicer, and PrusaSlicer, extrusion paths are considered oval rather than rectangular. This creates slight overlaps between adjacent walls, which can push outer walls outward and distort dimensions.
How It Works:
- When Precise Wall is OFF, the slicer uses overlapping paths to strengthen the print but slightly expands the wall outward.
- When Precise Wall is ON, the overlap is reduced to zero, keeping dimensions exact and walls uniform.
Advantages:
- Improved outer wall smoothness and dimensional accuracy.
- Better layer alignment and reduced surface irregularities.
- Works best with inner-to-outer wall order enabled.
Enable Precise Wall when accuracy matters more than extra infill density or print strength.
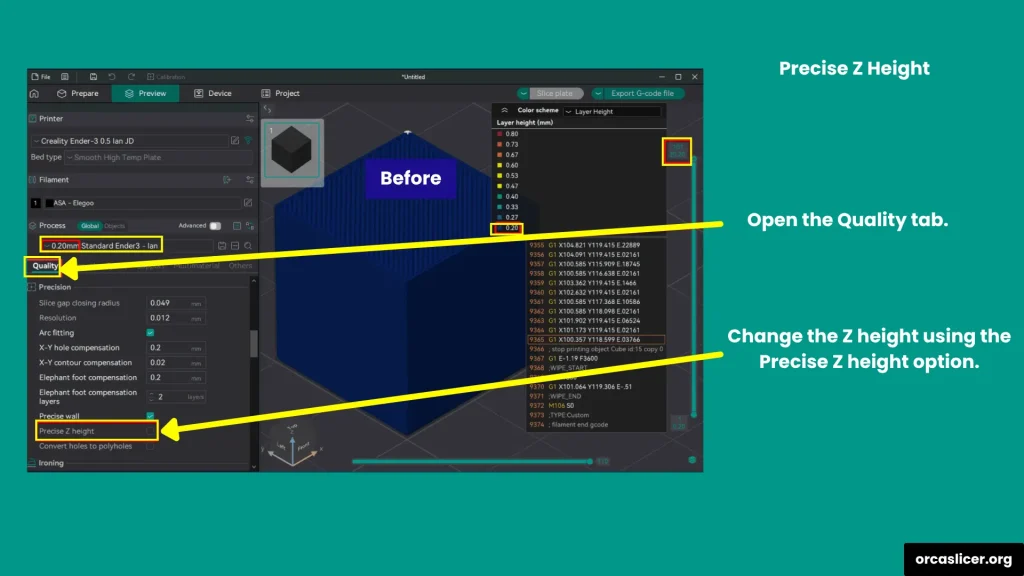
Precise Z Height
The Precise Z Height setting corrects small discrepancies between your model’s intended height and the actual printed result.
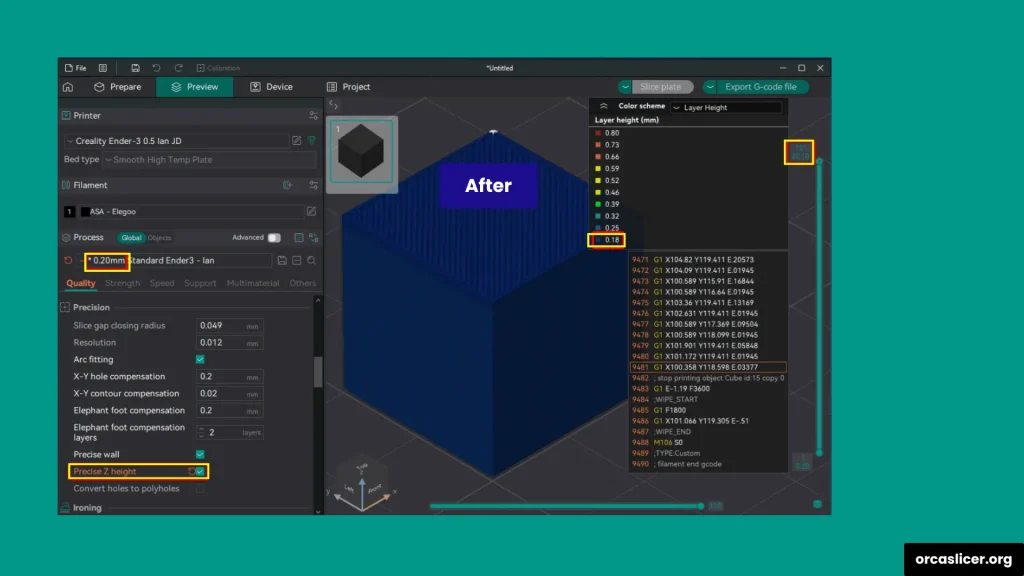
Example:
If your model measures 20.1 mm, but your layer height is 0.2 mm, the slicer rounds up, producing a 20.2 mm print. Enabling Precise Z Height allows Orca Slicer to slightly adjust the last few layer heights to perfectly match the model’s intended dimension.
Advantages:
- Ensures accurate Z-axis scaling.
- Corrects height mismatches in models with non-multiple layer increments.
- Ideal for functional parts requiring tight tolerances.
Example Setting:
If your model height is 20.1 mm and layer height is 0.2 mm → Enable Precise Z Height = 0.2 mm → final print = 20.1 mm exact.
PolyHoles
The PolyHoles technique improves the accuracy of circular holes in FFF printing. Because printers build shapes with flat segments, circular holes often print smaller than intended. PolyHoles solve this by representing the circle as a polygon made of tiny flat edges, allowing the slicer to print each edge precisely.

How It Works:
- The hole is divided into small, flat-sided segments.
- Each segment is treated as a linear path, which the printer executes more accurately than continuous arcs.
- The final hole fits the intended diameter closely.
Advantages:
- Accurate hole diameters for mechanical parts.
- Better dimensional consistency in circular openings.
- Perfect for models with pins, bolts, or joints requiring precision fit.
Pro Tip: Experiment with different polygon segment counts to balance print smoothness and dimensional accuracy.