Orca Slicer Guide
Orca Slicer is a user-friendly slicing software that works like a bridge between your 3D design and the printer. It takes your digital model and turns it into real objects, layer by layer, with accuracy.
In this guide, we’ll show you some of the most useful features of Orca Slicer. You’ll learn how to update the software, add supports, edit G-code, resize models, change print speed, switch nozzle sizes, cut and join objects, add a pause during printing, and save or export your settings.
How Does This Advanced 3D Printing Slicer Work?
OrcaSlicer takes your 3D model and cuts it into very thin layers. These layers are then turned into a special code, called G-code, which your 3D printer can read. This code tells the printer exactly how the nozzle should move, how much filament to use, what temperature to set, and more.
To avoid printing errors or mistakes, the software shows a preview of each layer after slicing. You can adjust settings like layer height, print speed, supports, and other options to make sure your prints look great. Once everything looks good, you can save the G-code file and send it to your printer through an SD card, USB, or Wi-Fi.
How to Update Orca Slicer?
Keeping Orca Slicer up to date is very important if you want the best print quality and smooth performance. Every new version comes with bug fixes, new features, and better stability. We’ll explain step by step how to update Orca Slicer safely without losing your settings.
Step 1: Check Your Current Version
Before you update, it’s good to know which version you are already using.
- Open Orca Slicer.
- Go to the Help or About section.
- Note down the version number.
Now, compare it with the latest version available on our site or the Orca Slicer GitHub releases page. If your version is older, then it’s time to update.
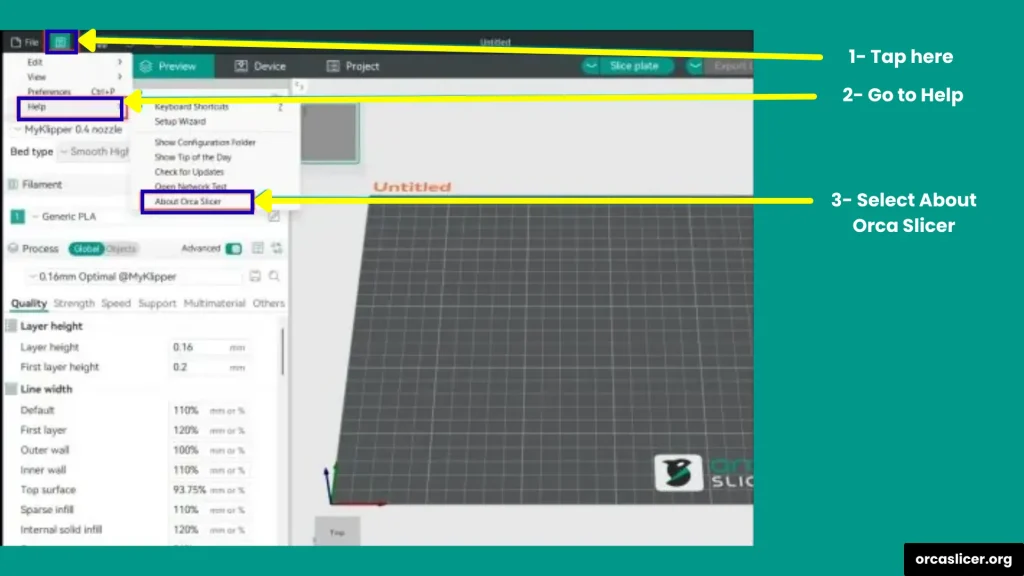

Step 2: Back Up Your Settings
It’s always smart to make a backup of your slicer settings before updating. This way, you won’t lose your custom profiles or printer configurations.
- Click on File in the toolbar.
- Select Export.
- Save the backup file in a safe place (like a separate folder, USB, or cloud storage).
Backing up saves you from the hurdle of setting up everything again after the update.
Step 3: Download the Latest Version
Now, it’s time to get the newest version of Orca Slicer.
- Visit our homepage to download latest version of Orca Slicer
- Choose the right version for your operating system (Windows, Mac, or Linux).
- Download the file.
Step 4: Install the Update
Once the download is complete, you can start the installation.
- First, close Orca Slicer if it’s running.
- Find the downloaded file in your system.
- Double-click the file to start the installation.
- Follow the step-by-step instructions on your screen until the installation is done.
After that, open Orca Slicer to make sure everything is working smoothly.
Step 5: Verify the Update
To confirm that you have the latest version:
- Open Orca Slicer again.
- Go to Help or About and check the version number.
- Explore the new features and check if the old bugs are fixed.
If everything looks good, you’re ready to slice and print with better performance.
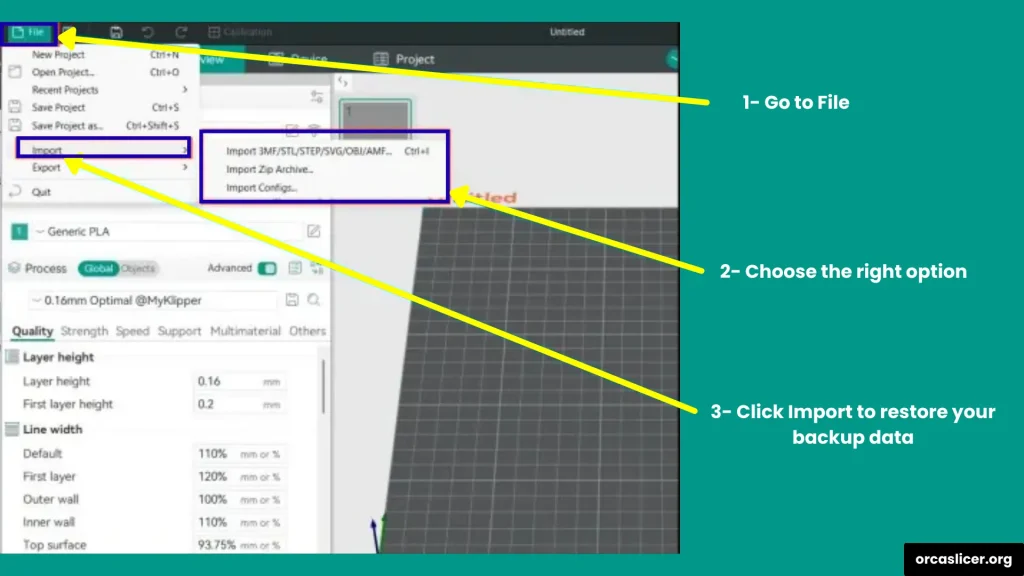
Step 6: Restore Your Backup (Optional)
If you want to bring back your old settings:
- Go to File in the toolbar.
- Select Import.
- Choose the backup file you saved earlier.
Your custom profiles and printer settings will be restored in the new version.
How to Edit G-code in Orca Slicer?
Editing G-code in Orca Slicer gives you more control over your 3D printer. By changing or adding commands, you can customize how your printer behaves before, during, and after a print. This can help improve print quality, add new functions, or even fix small issues.
Note: Always make a backup of your settings and test your changes on a small print first. That way, you won’t waste time or filament if something goes wrong.
Method 1: Edit Start or End G-code in Orca Slicer
The easiest way to edit G-code is directly inside Orca Slicer. This is useful when you want the printer to follow certain commands every time a print starts or ends.
Steps
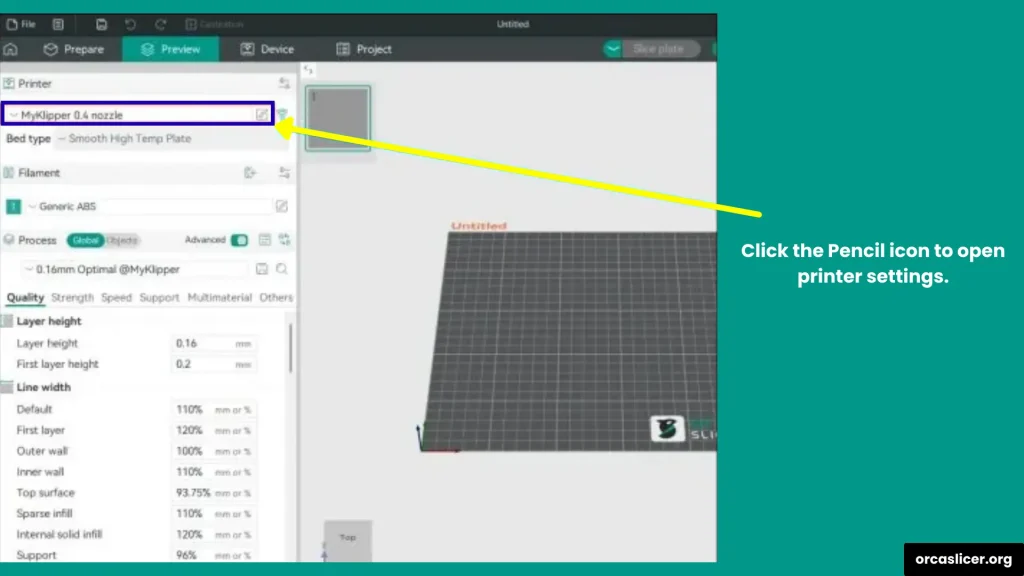
- Open Orca Slicer.
- Go to Printer Settings.
- Select Customize G-code.
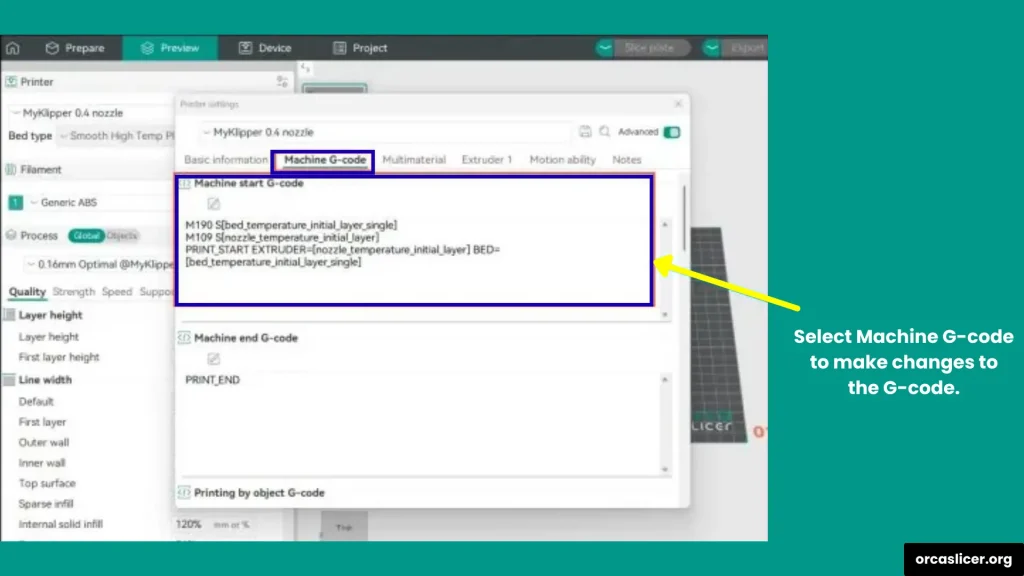
- Edit the Start G-code (commands that run before printing begins).
- Example: Heating the nozzle or moving the printer head to the home position.
- Edit the End G-code (commands that run after printing ends).
This method is great for adding general rules that apply to all your prints.
Method 2: Edit a Saved G-code File
If you want to make changes to a specific print, you can edit the exported G-code file using a text editor.
Steps
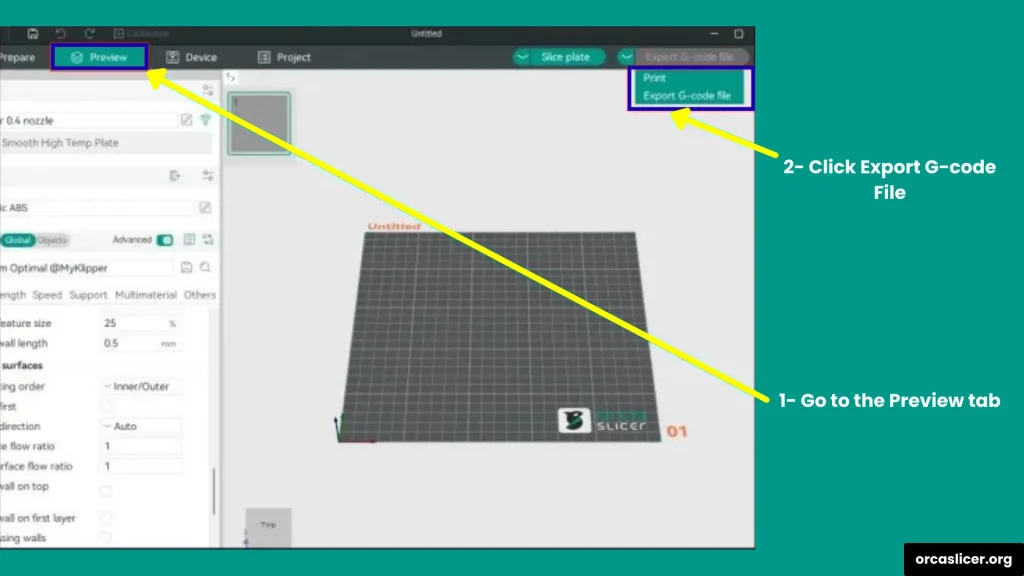
- Slice your model in Orca Slicer as usual.
- Go to the Preview tab and click Export G-code.
- Open the saved G-code file with a text editor such as Notepad++ or VS Code.
- Find the section you want to change and add your commands.
Examples of useful G-code commands
- M25 → Pause the print.
- M104 S210 → Set nozzle temperature to 210°C.
- M106 S255 → Turn the cooling fan on at full speed.
This method gives you detailed control over a single print without changing your default printer settings.
Method 3: Add Commands at a Specific Layer
Sometimes, you may want to run a command at a particular layer of your print. This is helpful if you want to pause at a certain height, change filament, or adjust fan speed.
Step
- Export your model as G-code from Orca Slicer.
- Open the file in a text editor.
- Search for a line like: LAYER:10.
- Add your custom command right after that line.
For Example
- At LAYER:10, you could add M600 to trigger a filament change.
This lets you create advanced print effects and more personalized results.
How to Shrink or Scale Models in Orca Slicer?
Sometimes a 3D model may be too big to fit your printer’s build plate or too small to print correctly. In these cases, you can shrink or scale your model in Orca Slicer with just a few clicks. Scaling lets you adjust the size of your object while keeping the correct proportions or changing specific dimensions like width, height, or depth.
Step 1: Load Your Model
- Open Orca Slicer on your computer.
- Click Add Model or drag and drop your 3D file into the workspace.
- Select the model you want to resize by clicking on it.
Step 2: Use the Scale Tool
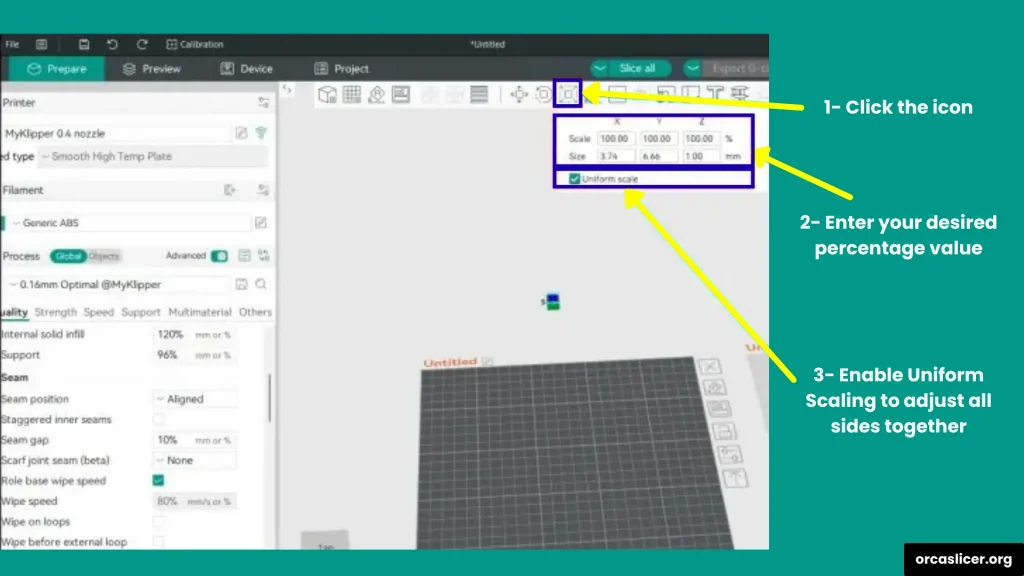
Once your model is selected, look at the toolbar on the side. You’ll see the Scale tool.
- To shrink your model, enter a percentage below 100% (for example, 50% will reduce it to half its original size).
- If you want to make it larger, enter a percentage above 100% (for example, 150% will make it one and a half times bigger).
Tip: You can also resize visually by dragging the scale handles on the model. This is useful if you prefer adjusting by eye rather than typing numbers.
Step 3: Uniform vs. Non-Uniform Scaling
Orca Slicer gives you two options for resizing:
- Uniform Scaling (On): This maintains the same proportions in all directions (width, height, and depth). It’s the best option if you want your model to look exactly the same, just bigger or smaller.
- Uniform Scaling (Off): This lets you adjust only one side of the model, like making it taller, wider, or flatter.
Step 4: Check the Preview
After scaling, always check the preview to make sure:
- The model fits on the build plate.
- It doesn’t exceed the printer’s maximum build volume.
- The size looks right for your project.
If everything looks good, move on to slicing your model.
Step 5: Slice and Export G-code
When you’re satisfied with the new size:
- Click Slice.
- Preview the sliced layers to confirm everything looks correct.
- Export the G-code and send it to your printer.
Your resized model is now ready to print.
How to Change Print Speed in Orca Slicer?
Print speed is one of the most important settings in 3D printing. If the speed is too high, you may get rough surfaces or failed prints. If it’s too low, the print may take a very long time. Luckily, Orca Slicer makes it easy to change print speed for different parts of your model.
Step 1: Open Your Model and Print Settings
- Launch Orca Slicer.
- Load the model you want to print.
- Go to the Print Settings tab.
- Scroll down or use the search bar to find the Speed section.
Here, you’ll see different speed options for each part of your print.
Step 2: Adjust Speed for Different Print Parts
In Orca Slicer, you can control the speed for each section of the print instead of using a single speed.
- Perimeters (Outer and Inner Walls): These are the outer surfaces of your model. Printing slower here improves quality. Example: 25 mm/s for walls, while infill is faster.
- Infill: This is the inside of your model that gives it strength. Since it’s not visible, you can print it faster. Example: 50 mm/s.
- Supports: Supports help your model print correctly. You can match them to infill speed or slow them down a little if the model has fine details.
- Travel Moves: These are non-printing moves when the nozzle travels between sections. They can stay fast to save time.
Tip: A common setup is 25 mm/s for walls and 50 mm/s for infill/supports. But you can experiment depending on your printer and material.
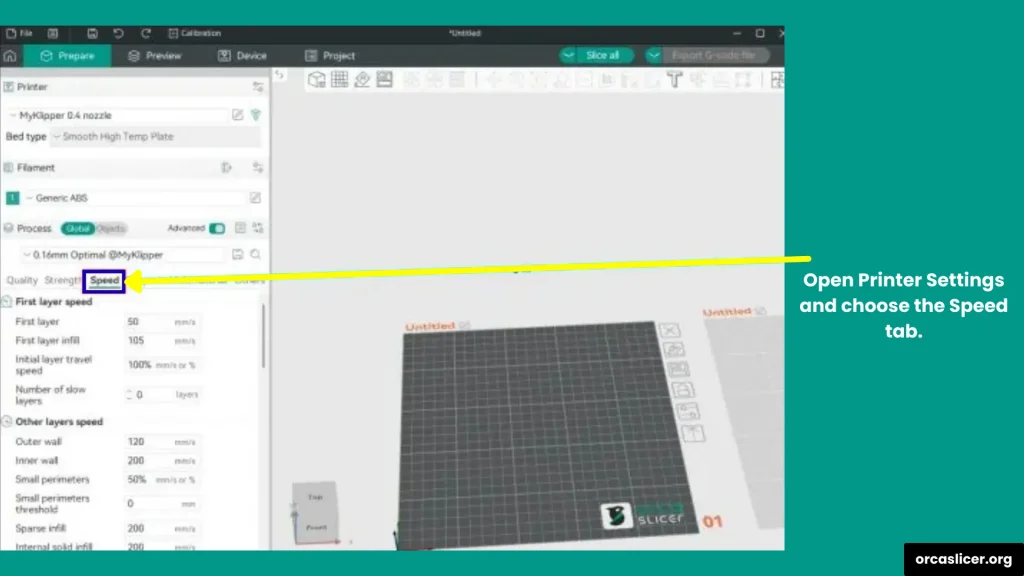
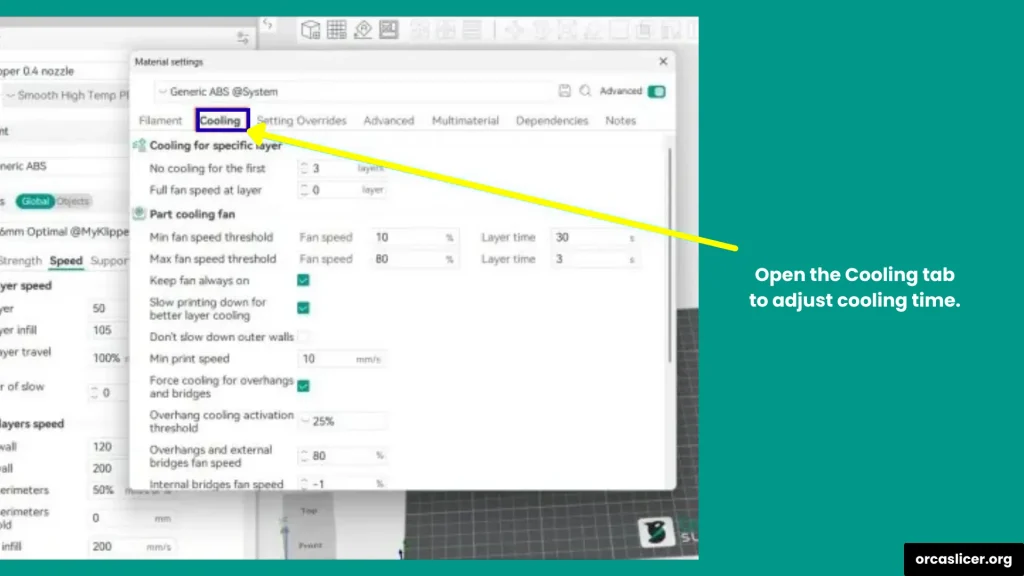
Step 3: Cooling and Small Layer Speed
Orca Slicer automatically slows down very small layers to let them cool before the next one starts. You can adjust this in:
- Cooling → Minimum Layer Time
For example, if you notice tiny layers melting or deforming, increasing the minimum layer time will help.
Step 4: Check Maximum Volumetric Flow
Sometimes, even if you set a high speed, the printer may not actually reach it. That’s because of your hotend’s maximum volumetric flow (the amount of filament it can melt per second). If Orca Slicer limits your speed, check your printer profile and adjust the maximum volumetric flow to match your hardware.
Step 5: Understand Acceleration and Real Speed
Remember that print speed is not only about the number you set. Acceleration settings also affect how fast your printer can move.
- If the acceleration is too low, the printer won’t reach the full speed, especially for small moves.
- For larger, simple shapes, higher speeds are easier to achieve.
Note: You can tune acceleration and jerk settings in your firmware for even more control.
How to Change Nozzle Size in Orca Slicer?
The nozzle size of your 3D printer directly affects both print speed and print quality. Smaller nozzles create fine details but take longer, while larger nozzles print much faster but with less detail. In Orca Slicer, changing the nozzle size is simple and allows you to adjust your prints for different needs.
Why Nozzle Size Matters in 3D Printing
Different nozzle sizes give different results:
- 0.2 mm nozzle → Prints very slowly but produces high detail and smoother surfaces.
- 0.4 mm nozzle (default) → Balanced option for speed and detail.
- 0.6 mm nozzle → Prints faster, good for larger models, but loses some detail.
- 0.8 mm nozzle → Very fast printing, but less accurate details.
Choosing the right nozzle size depends on whether you want speed or detail in your print.
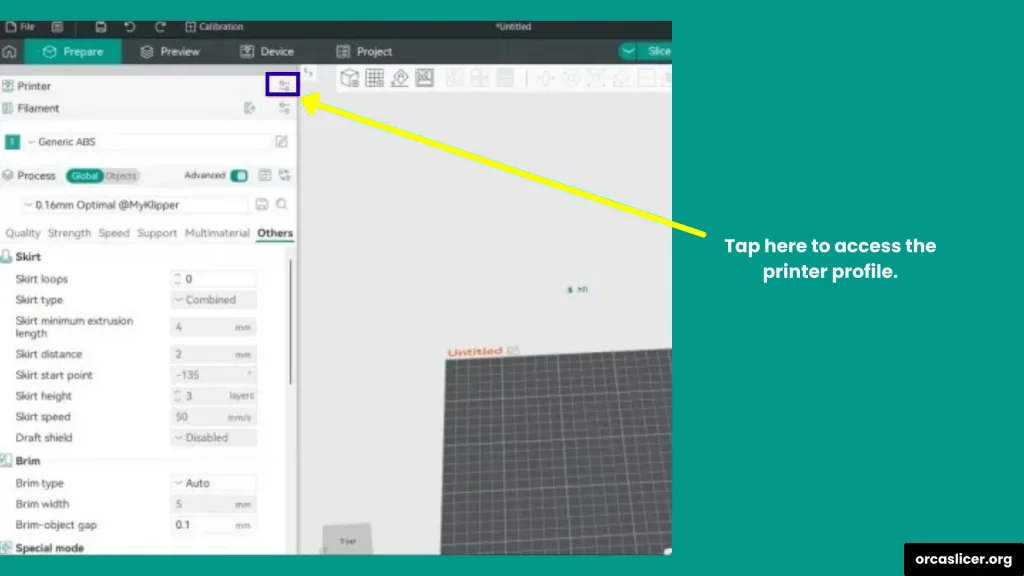
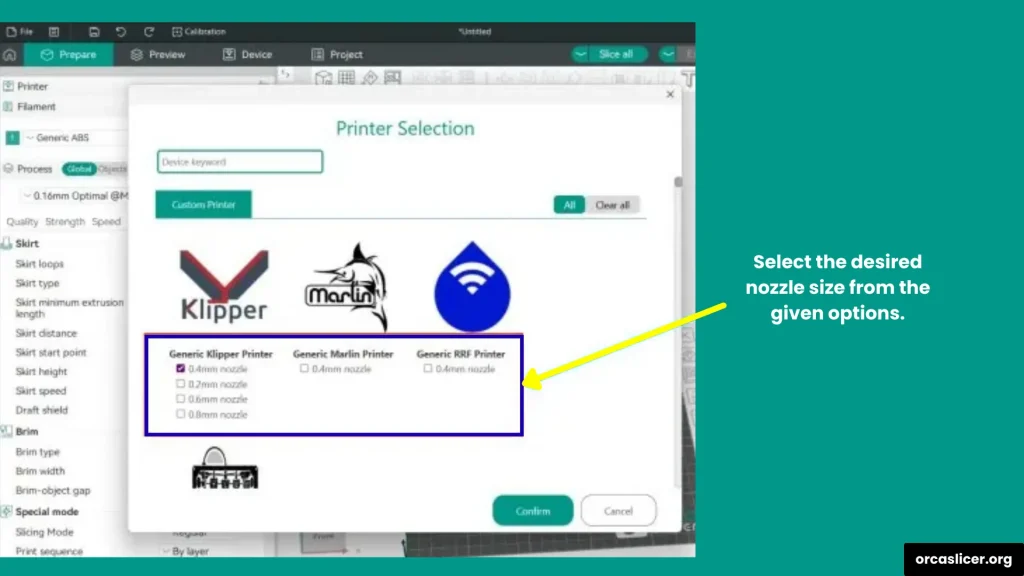
Step 1: Open Orca Slicer and Printer Profile
- Launch Orca Slicer on your computer.
- Go to your Printer Profile (this is where your printer’s hardware settings are saved).
Step 2: Change Nozzle Diameter
- Open Printer Settings.
- Look for the Nozzle Diameter option.
- Select the nozzle size you want from the list (e.g., 0.2 mm, 0.4 mm, 0.6 mm, or 0.8 mm).
- Click Save to keep the changes.
Step 3: Fine-Tune Print Settings
After swapping the nozzle, you must adjust your print settings to match the new size. If you skip this, you may end up with poor quality or wasted time.
- Layer Height: Should be about 25–75% of nozzle size. Example: With a 0.4 mm nozzle, use 0.1–0.3 mm layer height.
- Print Speed: Larger nozzles can handle faster speeds. Smaller nozzles should print slower for accuracy.
- Extrusion Width: Update this so the slicer knows how wide each line of filament will be.
Always run a test print after changing the nozzle size to make sure the results match your expectations.
How to Cut Models in OrcaSlicer?
Sometimes, your 3D model is too big for the print bed, or you want to create parts that can be glued or clicked together later. That’s when the Cut function in OrcaSlicer becomes really useful. This feature lets you split a model into multiple parts and even add connectors so pieces fit together perfectly.
Step 1: Open OrcaSlicer
Start by launching OrcaSlicer on your computer. The interface might look slightly different depending on which version you’re using, but the cutting process works the same way.
Step 2: Import Your 3D Model
- Click Add Model or simply drag and drop your 3D file into OrcaSlicer.
- Select the model you want to cut.
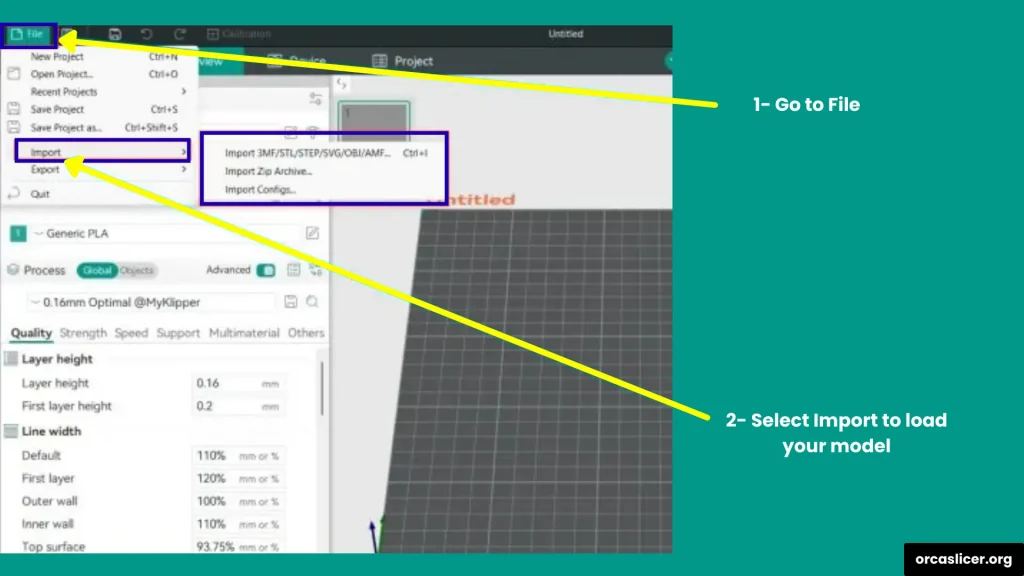
Step 3: Open the Cut Tool
- Highlight your model by clicking on it.
- Use the shortcut Shift + C to activate the Cut function.
- OrcaSlicer will automatically create a cut line through your model.
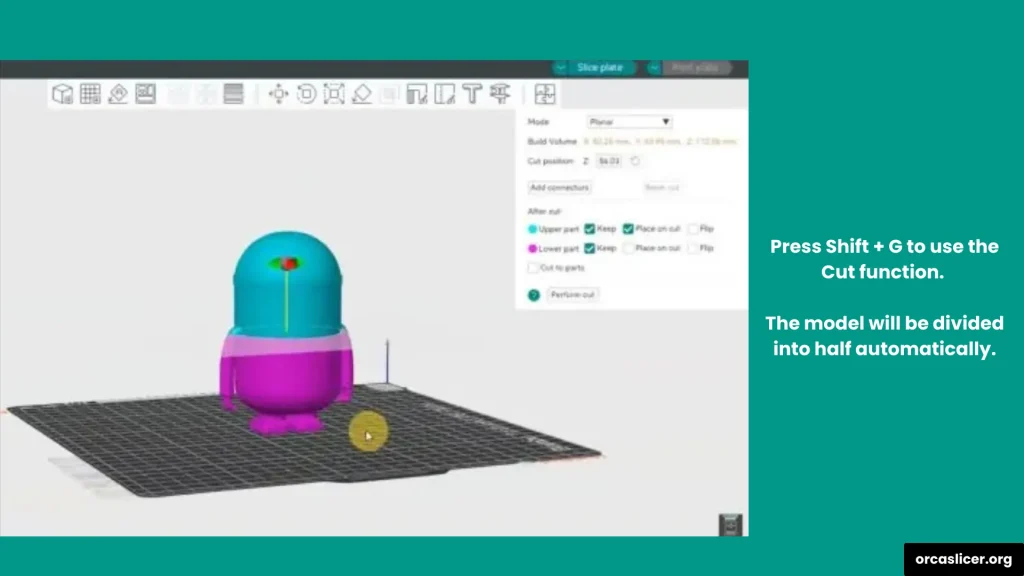
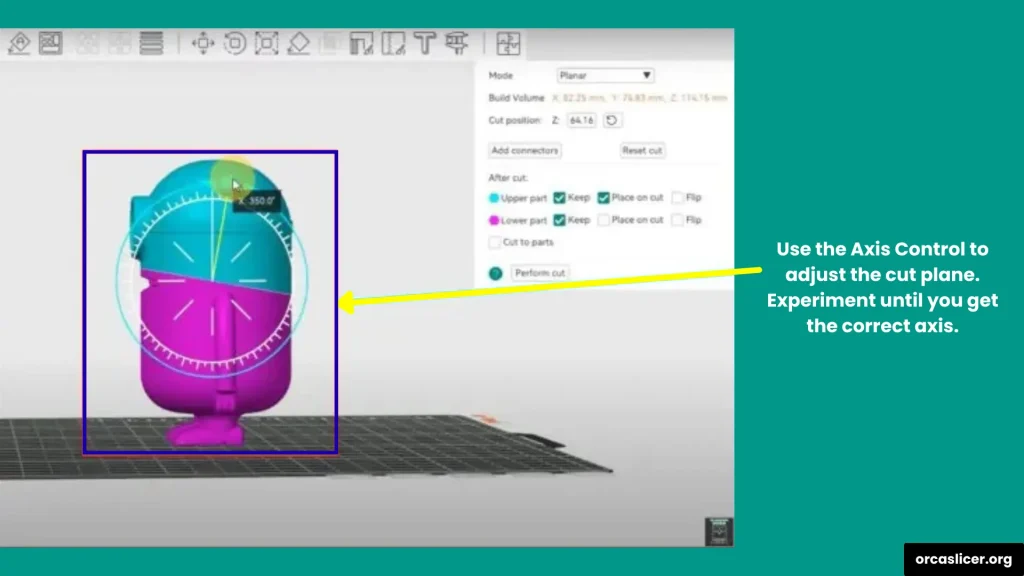
Step 4: Adjust the Cut Line
- Look carefully at where the slicer has placed the cut.
- If it’s not where you want it, use the axis controls (X, Y, Z) to move the cutting plane.
- You can also rotate the cut plane for angled cuts.
Experiment with the cut position until you’re satisfied. This gives you full control over how the parts will be split.
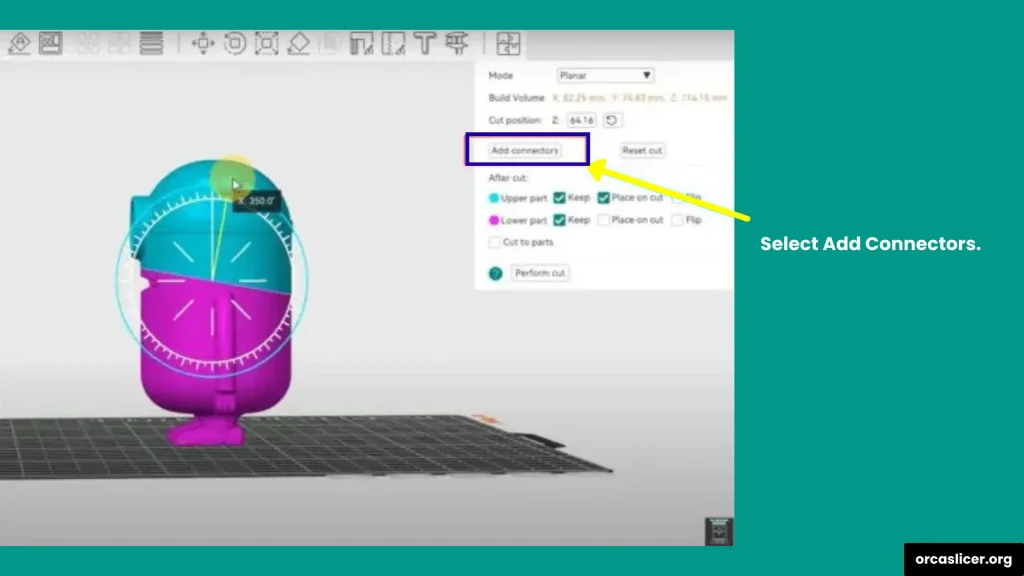
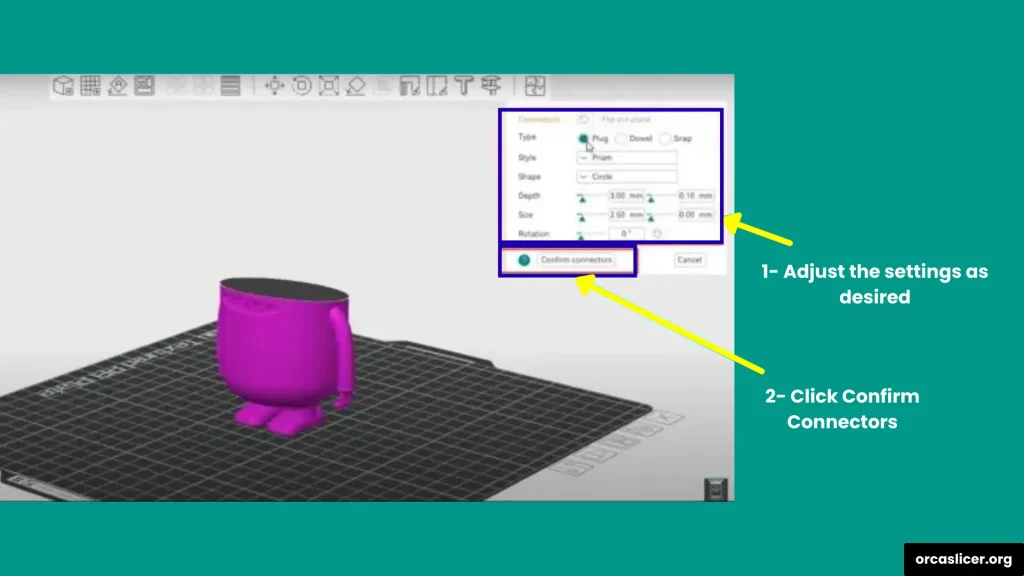
Step 5: Add Connectors (Optional but Recommended)
One of the best features in OrcaSlicer is the ability to add connectors between the parts:
- Click Connectors in the menu.
- Choose where you want the connectors to be placed.
- Adjust their size, depth, and shape. For example:
- Round connectors → Easy to print and align.
- Hexagon connectors → Stronger grip and better fit.
- The deeper the connector, the stronger the joint will be.
Once you’re satisfied, click Confirm Connectors. OrcaSlicer will apply them, and the model will appear whole again (but internally split with connectors).
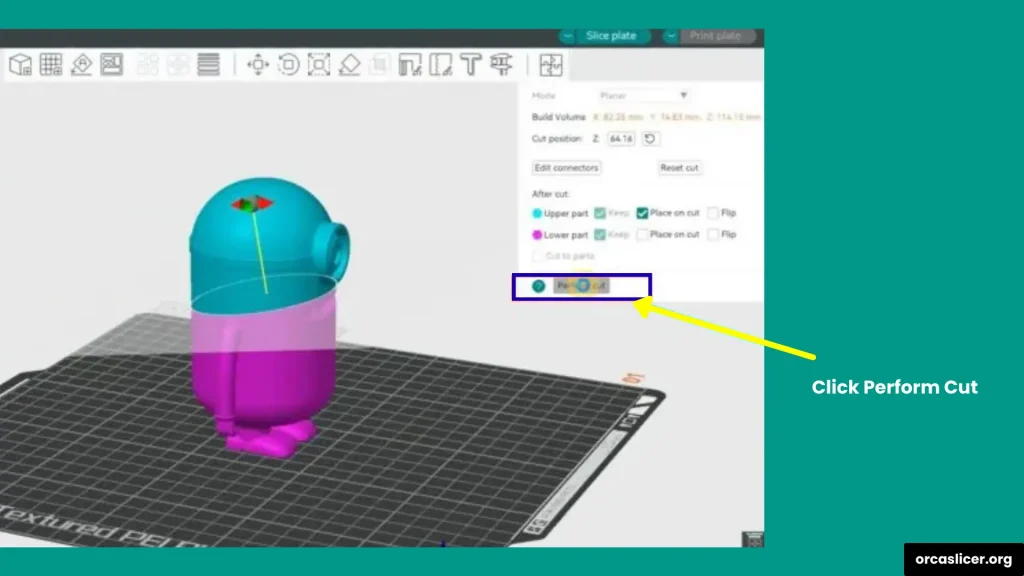
Step 6: Perform the Cut
- Finally, click Perform Cut.
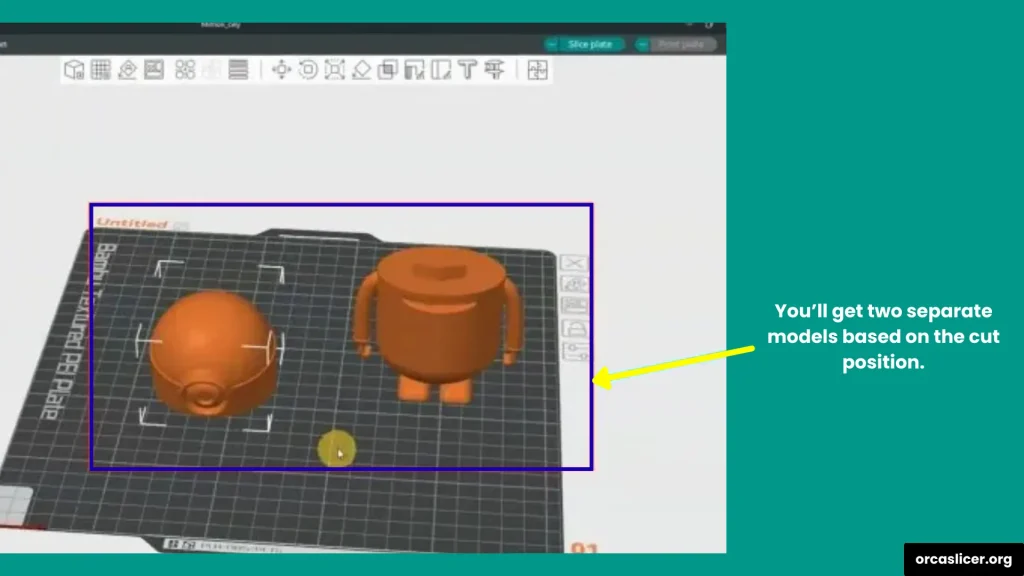
- The model will now be separated into two or more pieces based on your cut line.
- Each piece will act as its own part, ready for slicing and printing.
How to Merge Objects in OrcaSlicer
Merging objects in OrcaSlicer is very useful when you have multiple parts that you want to print as a single model. This feature comes from Bambu Studio and makes it easier to combine models without needing extra 3D design software.
Step 1: Import Your Models
- Open OrcaSlicer on your computer.
- Click Add Model or drag and drop the files into the build plate.
- You can import as many models as you need to merge.
Note: Make sure all the models are scaled correctly before merging.
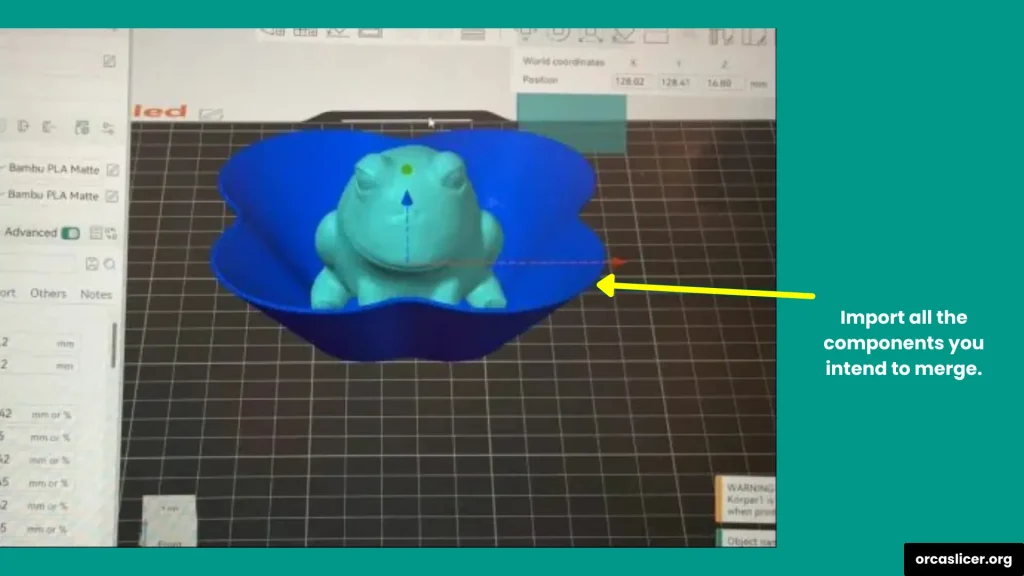
Step 2: Position the Models
- Move, rotate, or align the models on the build plate so they fit exactly how you want.
- For clean merging, make sure the models slightly overlap or touch each other.
- You can use the Move tool and Rotate tool from the side toolbar for better placement.
If models don’t overlap, they won’t stick together after merging.
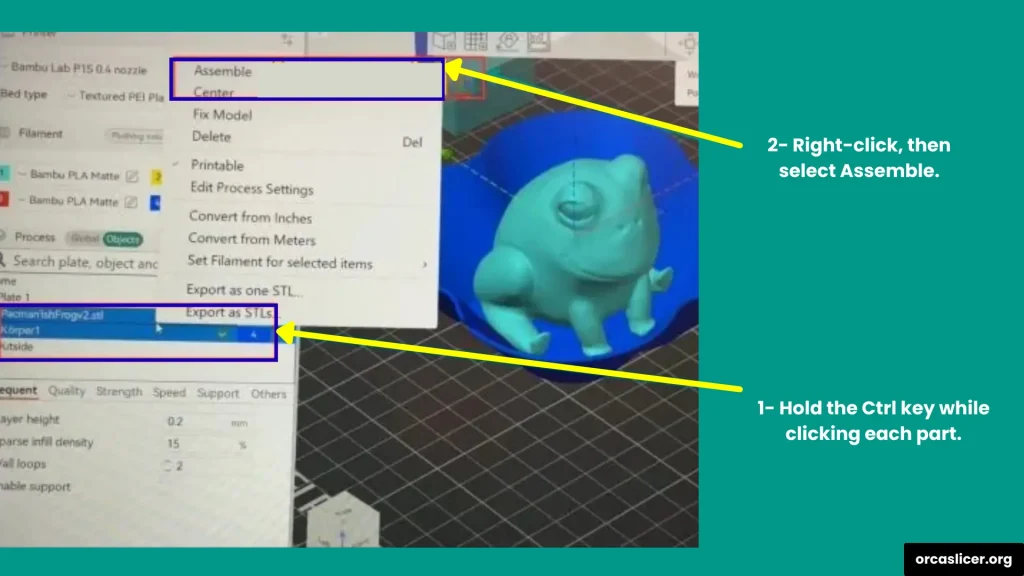
Step 3: Assemble the Models
- Select all the models you want to merge.
- Hold Ctrl and click each one on the build plate, or Select them directly from the Object List on the left side.
- Right-click and choose Assemble.
Now, OrcaSlicer will treat them as one object during slicing, but you can still edit or reposition individual parts if needed.
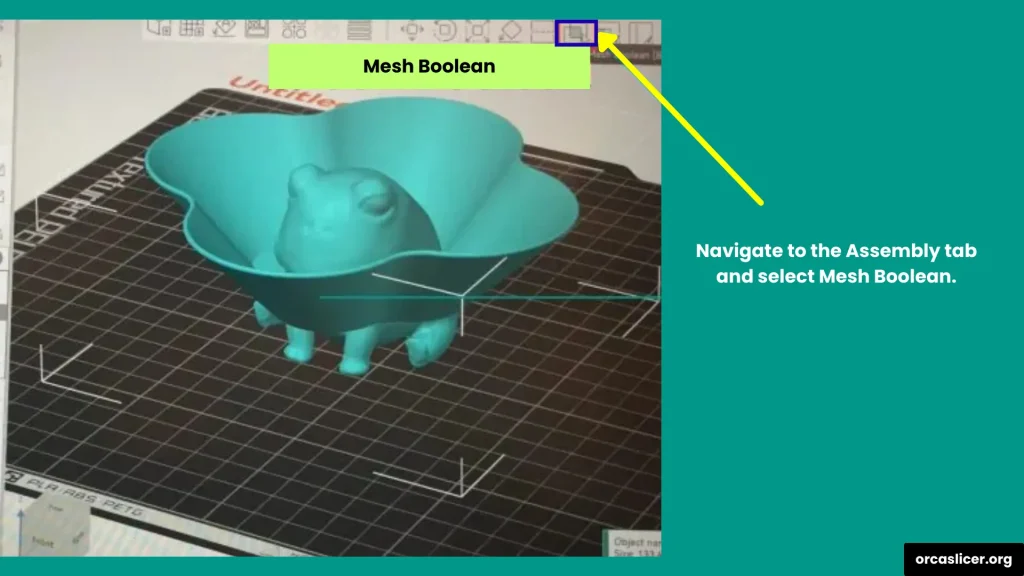
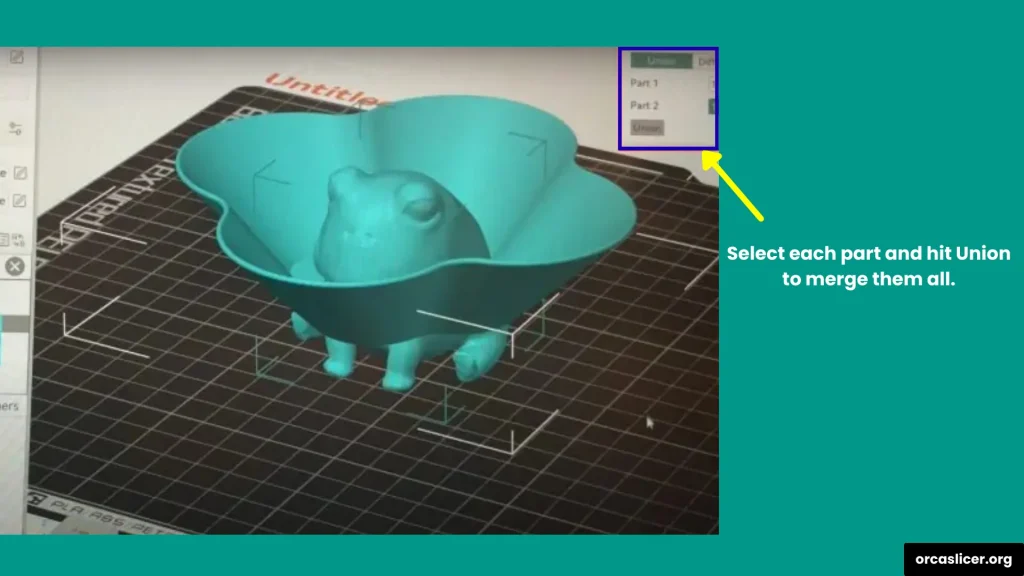
Step 4: Combine into a Single Solid Mesh
To make the models fully combined into one piece (instead of just grouped), you need to create a solid mesh:
- On the left-hand side, go to Assembly.
- Choose Mesh Boolean → Union.
- Select the parts you want to combine.
- Click Union.
The process may take a few seconds, depending on the size of your models. Once finished, you’ll have a single solid object ready for slicing.
How to Add a Pause in OrcaSlicer?
Sometimes, you may want your 3D printer to pause in the middle of a print. This is useful if you want to:
- Change filament colors for multi-color prints
- Insert nuts, magnets, or other objects inside your model
- Inspect the print quality before it continues
With OrcaSlicer, adding a pause is simple and doesn’t require manual G-code editing. Here’s how you can do it step by step.
Step 1: Import Your Model
- Open OrcaSlicer on your computer.
- Click Add Model or drag and drop your 3D file onto the build plate.
- Make sure your model is oriented and scaled properly before moving on.
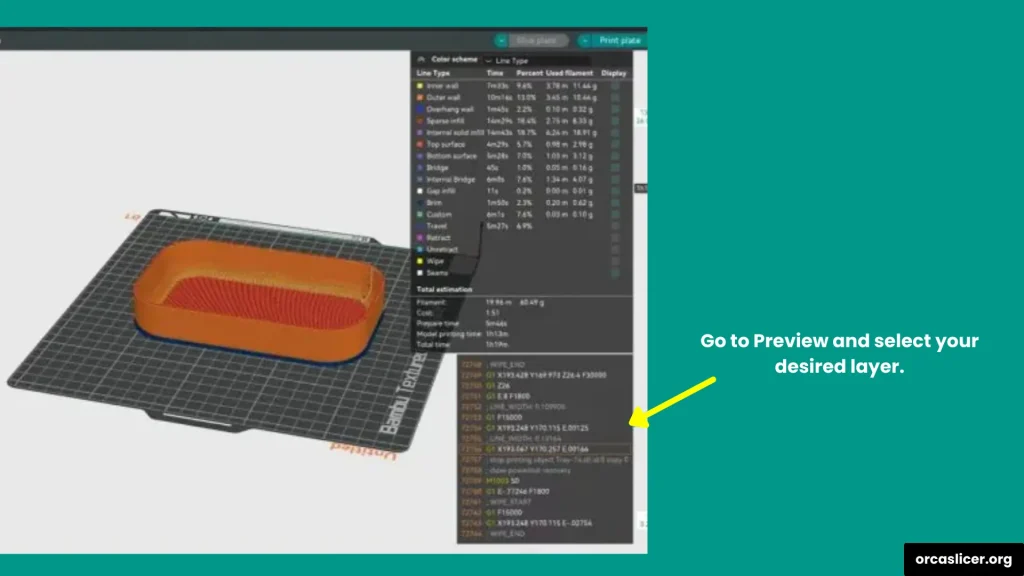
Step 2: Preview the Layers
- Once your model is ready, click on the Preview Tab (top right).
- Here, you can scroll through each layer of the print from bottom to top.
- Carefully look at where you want to add a pause.
Example: before a new color starts, or right before closing the top of a cavity where you want to place an object.
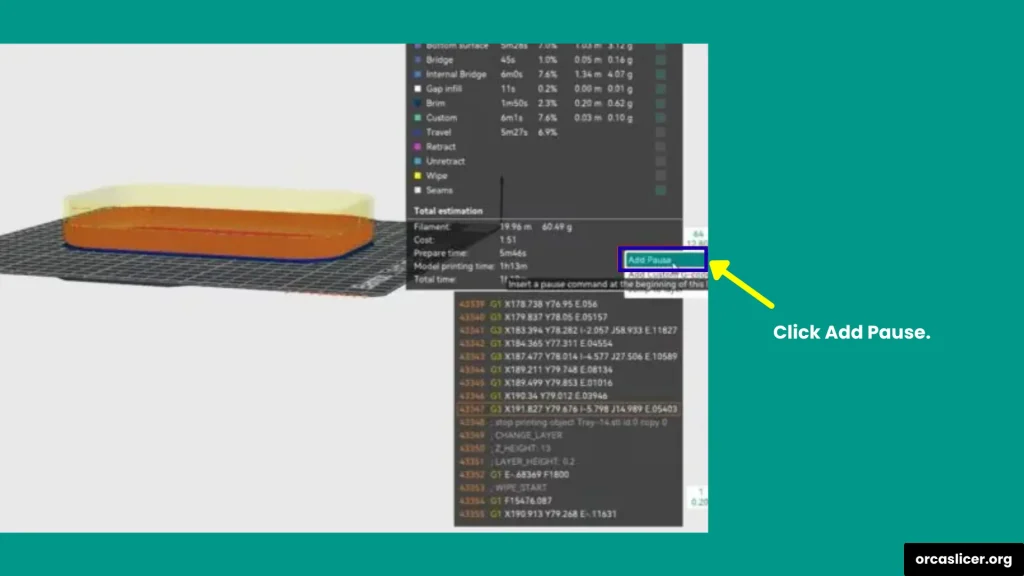
Step 3: Add the Pause Command
- In the Preview tab, right-click on the layer where you want the printer to stop.
- From the menu, select Add Pause.
- OrcaSlicer will now insert a pause command (like M25 or M0) into the G-code at that exact layer.
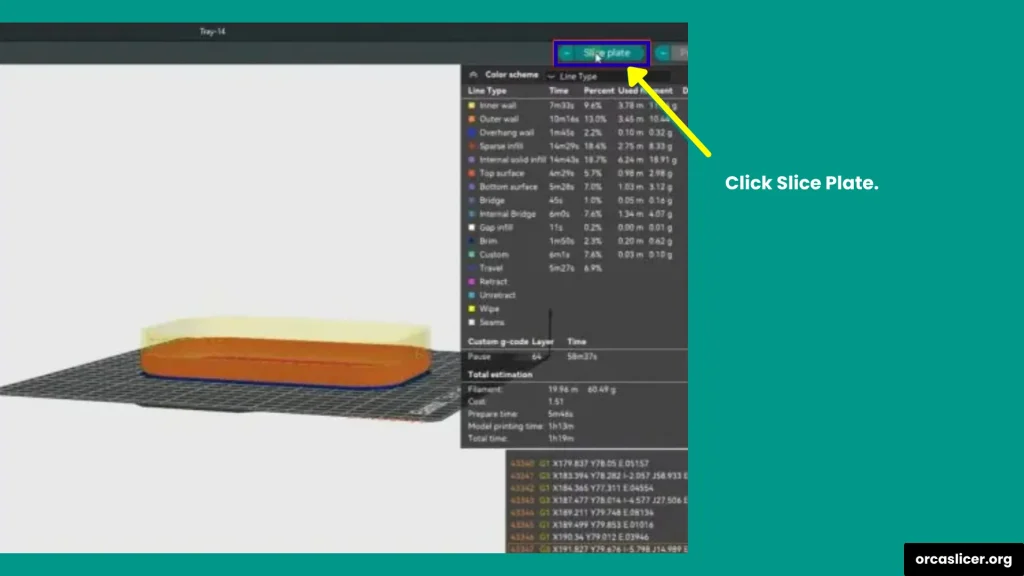
Step 4: Reslice the Model
- After adding the pause, click Slice Plate in the bottom-right corner.
- OrcaSlicer will reprocess the model and add the pause command to your final G-code file.
- You can then go back to Preview Mode to double-check that the pause is in place.
Step 5: Export and Print
- Export your G-code file and send it to your 3D printer (via SD card, USB, or Wi-Fi).
- When the printer reaches the pause layer: It will stop printing. The nozzle will move away from the part. The heaters may stay on (depending on your settings).
This gives you time to swap filament, insert parts, or make adjustments. Once you’re ready, simply press Resume on your printer’s screen.
How to Export Orca Slicer Settings?
When you spend time fine-tuning your printer profiles, filament settings, or custom print processes in OrcaSlicer, it’s a smart idea to export those settings. This allows you to:
- Keep a backup of your profiles in case something goes wrong.
- Transfer settings to another computer.
- Share your optimized profiles with friends or the 3D printing community.
- Save time by reusing the same presets across multiple printers.
Here’s a simple way on how to export settings in OrcaSlicer.
Step 1: Open OrcaSlicer
- Launch OrcaSlicer on your computer.
- Make sure the printer, filament, and print profiles you want to export are loaded.
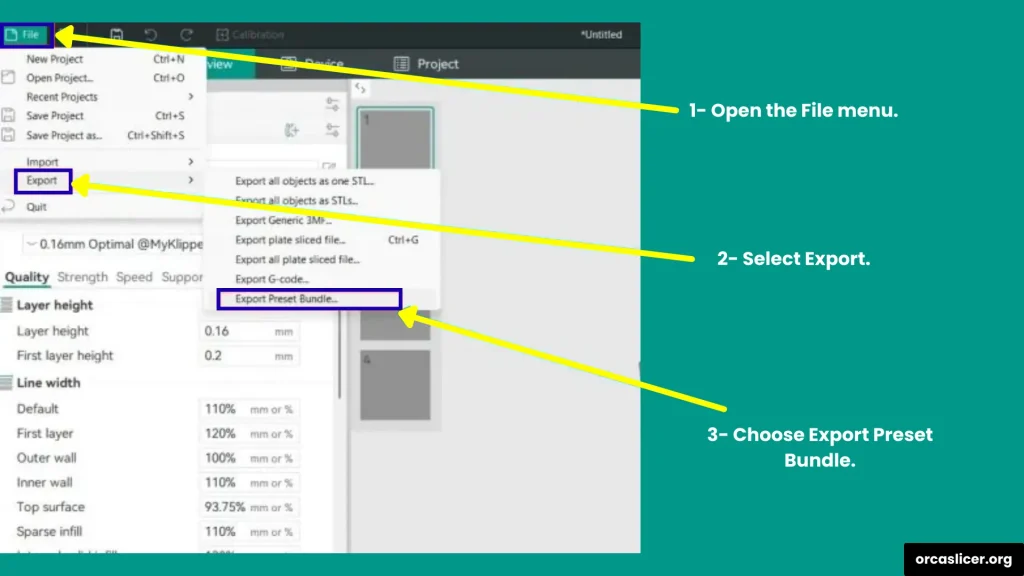
Step 2: Open the Export Menu
- Go to the top-left corner of the screen.
- Click on File → Export.
- From the dropdown menu, choose Export Preset Bundle.
This will open the export settings window.
Step 3: Choose What to Export
OrcaSlicer gives you several export options depending on what you need:
- Printer config bundle (.orca_printer) → Exports your complete printer setup, including custom printer settings, filaments, and print profiles.
- Filament bundle (.orca_filament) → Exports filament profiles with their printer connections.
- Printer presets (.zip) → Exports only printer configurations.
- Filament presets (.zip) → Exports only filament profiles.
- Process presets (.zip) → Exports print process settings, like layer height, speeds, or supports.
Choose the option that best fits your needs.
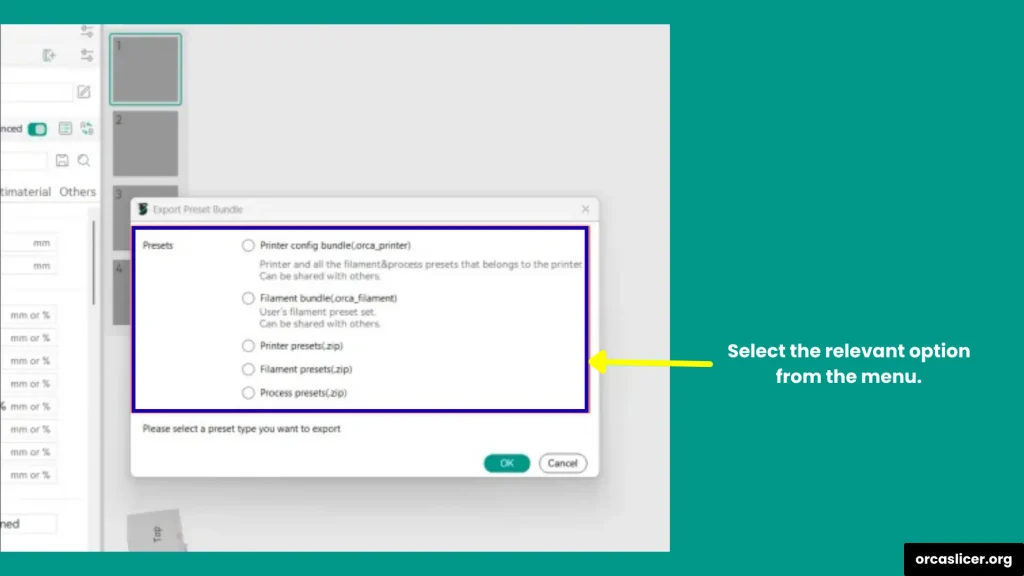
Step 4: Select the Presets
- After choosing the type of export, you’ll see a list of available presets.
- Check the boxes for the specific profiles you want to save.
- This is handy if you don’t want to export everything and only need certain profiles.
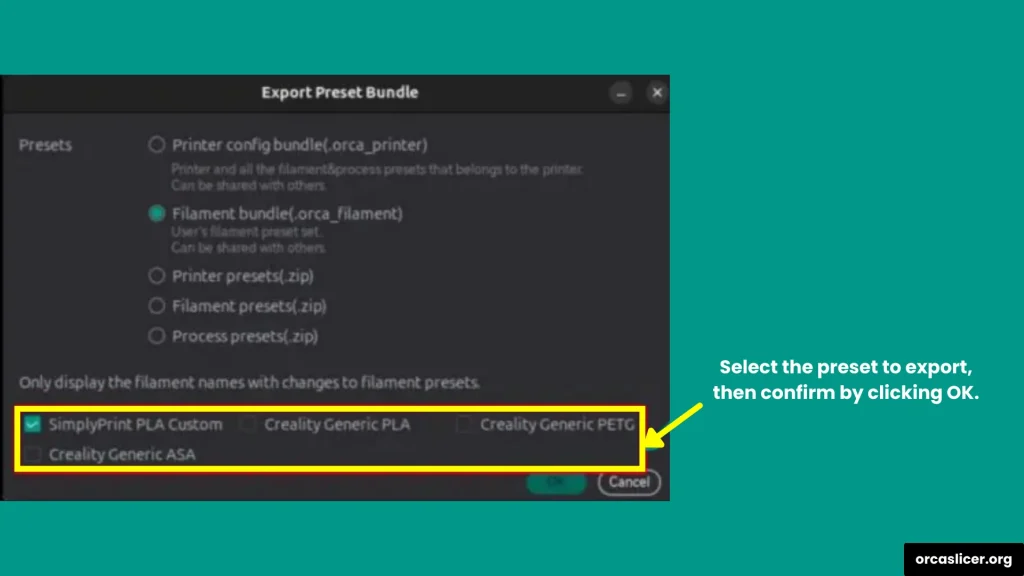
Step 5: Save the Exported File
- Click OK to confirm.
- A file manager window will pop up.
- Choose a folder where you can easily find the exported file later (for example, “3D Printing Settings” on your desktop).
- Give the file a clear name, and click Save.
Your settings are now safely exported and ready to use on another computer or share with others.
How to Add Supports in OrcaSlicer?
When 3D printing complex models with overhangs, bridges, or tall angles, you need supports to stop the print from sagging or failing. OrcaSlicer makes it simple to add automatic or custom supports, giving you more control over how your model prints.
Step 1: Open OrcaSlicer and Import Your Model
- Launch OrcaSlicer on your computer.
- Drag and drop your 3D model onto the build plate.
- Make sure it is positioned correctly before adding supports.
Step 2: Enable Automatic Supports
OrcaSlicer can generate supports for you automatically:
- Go to the Right Toolbar and click on the Supports icon.
- Select Generate Auto Supports.
- Orca will automatically detect overhangs and areas that need extra support.
Automatic supports are great for beginners, but sometimes they add too much material, which can be harder to remove.
Step 3: Add Custom Supports
If you want more control over where supports are placed, use the custom supports option:
- Go to the Preview or Editor tab.
- Right-click on the model and choose Add Support Block.
- Place the block exactly where you want support (for example, under a sharp overhang).
- Adjust the size, shape, and angle of the support block using the toolbar.
- You can add multiple supports wherever needed.
Step 4: Adjust Support Settings
For even better results, fine-tune support settings under Print Settings → Supports:
- Support Overhang Angle → Controls when supports are generated (default is usually 45°).
- Support Density → Lower density = easier to remove, higher density = stronger support.
- Support Pattern → Choose from grid, lines, or tree-style supports.
- Support Z Distance → Gap between support and model; bigger gap makes removal easier.
Step 5: Preview Your Supports
- After adding supports, click Slice.
- Switch to the Preview tab to check how supports look layer by layer.
- Make sure they don’t block small details or create unnecessary bulk.
Step 6: Print with Supports
- Once you’re satisfied with the support placement, export your G-code.
- Start your print and watch how the supports help the model stay stable.
- After printing, carefully remove the supports using pliers or cutters.
Conclusion
OrcaSlicer is a powerful and user-friendly tool that makes 3D printing easier, faster, and more exciting. From cutting models into parts, merging objects, adding pauses, exporting settings, and even placing supports, this slicer gives you full control over your prints. Each feature is designed to save time, improve print quality, and help you customize your projects the way you want.
Whether you are a beginner learning the basics or an advanced maker who wants precision, OrcaSlicer has everything you need. The best part is that it’s always improving with new updates, making it even more useful for the 3D printing community. By practicing the steps in this guide, you’ll be able to prepare your models like a pro and enjoy smoother, more successful prints.