Seam Settings
Seam settings in Orca Slicer play a key role in controlling both the visual appeal and surface quality of your 3D prints. A seam is the point where a single layer begins and ends during printing. In simpler terms, every layer has a starting point and an ending point, and this transition creates a visible line or mark on the print’s surface.
Only spiral or vase-like models are printed continuously without seams, as they are extruded in one uninterrupted motion. All other 3D models have seams, which can affect the final surface finish if not properly managed.
In Orca Slicer, two main factors influence seam quality:
- Seam Position
- Seam Modifiers
By adjusting these settings, you can hide, align, or minimize the seam marks to achieve a smoother and cleaner print.
Below, we will explore each seam setting element, offer professional optimization tips, and explain troubleshooting techniques to help you master seam control for flawless 3D printing results.
Seam Position Settings
Seam position defines where the start and end points of each layer appear on the printed model. Managing seam placement is essential for maintaining both aesthetic quality and structural strength. By positioning seams strategically, you can hide them in less visible areas or distribute them across layers to reduce weakness.
Seam Position Options
Aligned
Places all seams in the same vertical line across layers. This keeps the seam neat and easy to locate, often on the model’s backside. It’s ideal when visual consistency is preferred.

Aligned Back
Combines both alignment and backside placement. This setting directs seams to less visible areas, usually away from the front face, helping maintain surface beauty while keeping them organized.

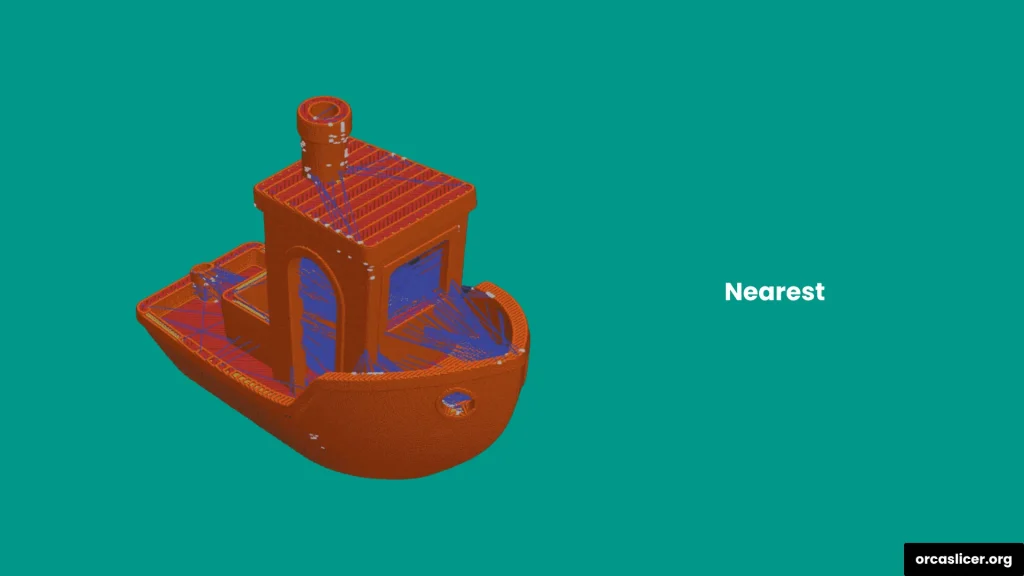
Nearest
Places the seam closest to the nozzle’s current position. It minimizes travel time and is best for faster prints where speed matters more than appearance.
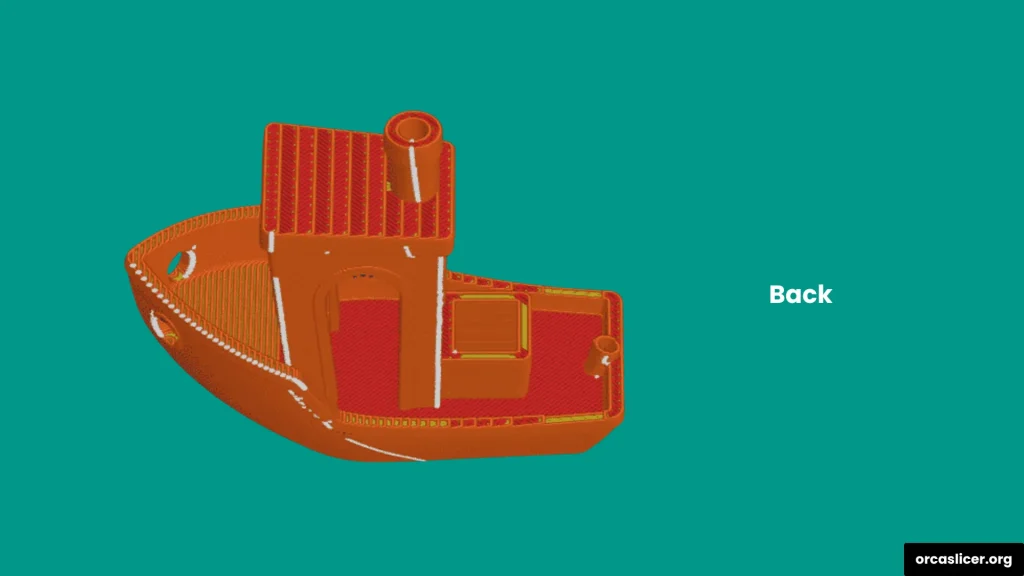
Back
Positions the seam toward the minimum Y direction (usually the model’s rear). This is useful when you want the front view of the object to remain smooth and visually clean.
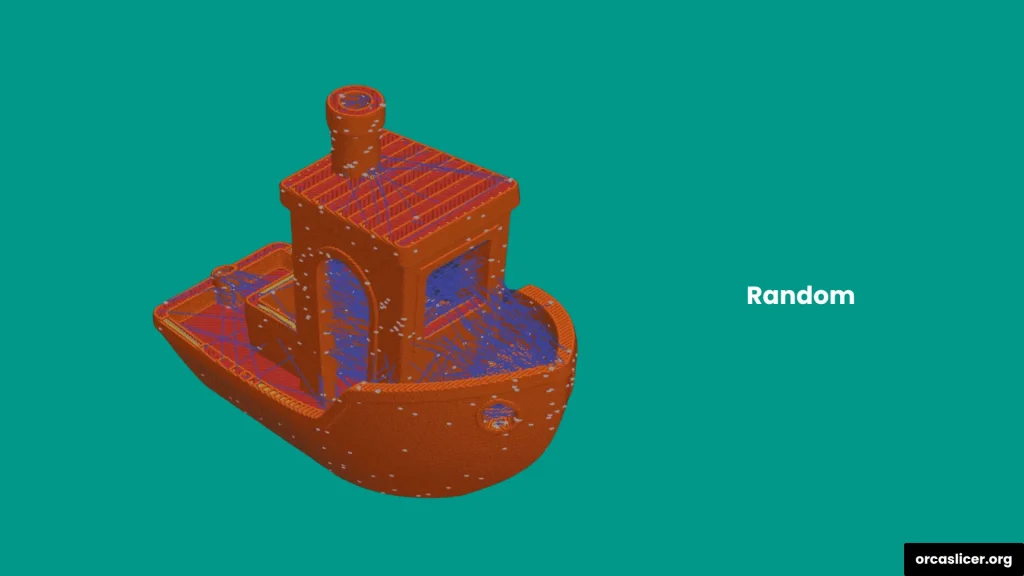
Random
Distributes seams randomly across the model’s surface. This setting prevents a visible line from forming and spreads out weak points, improving overall strength.
Pro Tip: If strength is a priority, use the Random option to distribute seams evenly and avoid stacking them in one place. If visual appearance is more important, use Aligned Back or Back to hide seams on less noticeable areas.
Seam Modifiers
In Orca Slicer, seam modifiers help you fine-tune and improve the strength, stability, and visual quality of your 3D prints. Since every seam is a potential weak point, these modifiers intelligently adjust how and where the seams are printed, minimizing visible marks and reinforcing the structure.
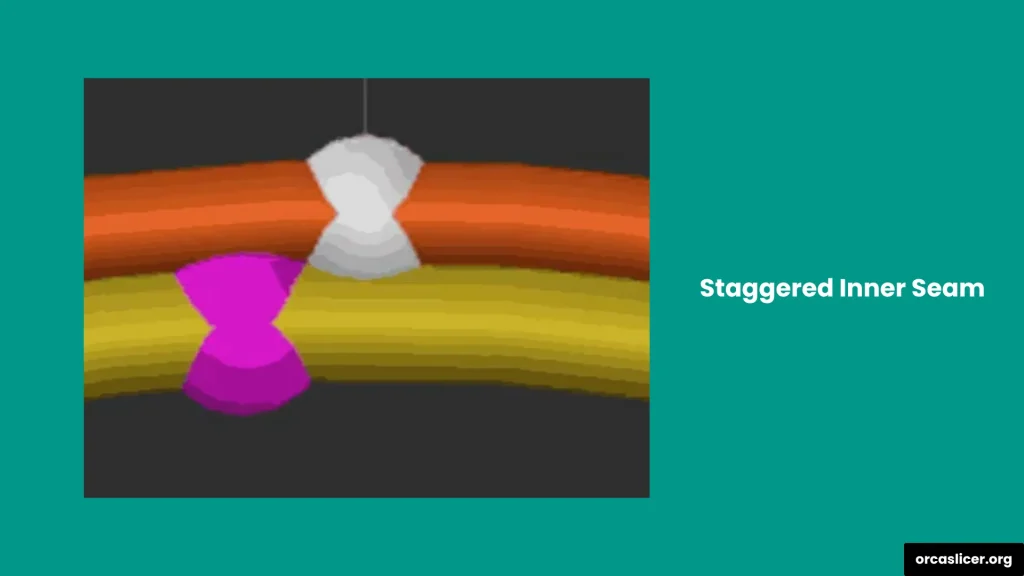
Staggered Inner Seam
A staggered inner seam uses an offset printing technique to avoid starting and ending each seam at the same point on every layer. Instead, it shifts the seam locations slightly in a non-linear pattern across internal perimeters.
This staggered pattern spreads the weak points across different areas, significantly improving the model’s overall strength. It also helps achieve better watertightness and reduced stress concentration, making it ideal for high-strength or functional prints.
Seam Gap
The seam gap controls the small distance between the start and end points of a seam. You can define this in millimeters or as a percentage of the nozzle diameter.
- A larger gap helps reduce bulging or overextrusion at the seam.
- A smaller gap minimizes seam visibility but may slightly affect surface finish.
Recommended Setting: Keep the seam gap between 0%–15% of the nozzle diameter for a well-tuned printer. This provides the right balance between visual appeal and structural consistency.

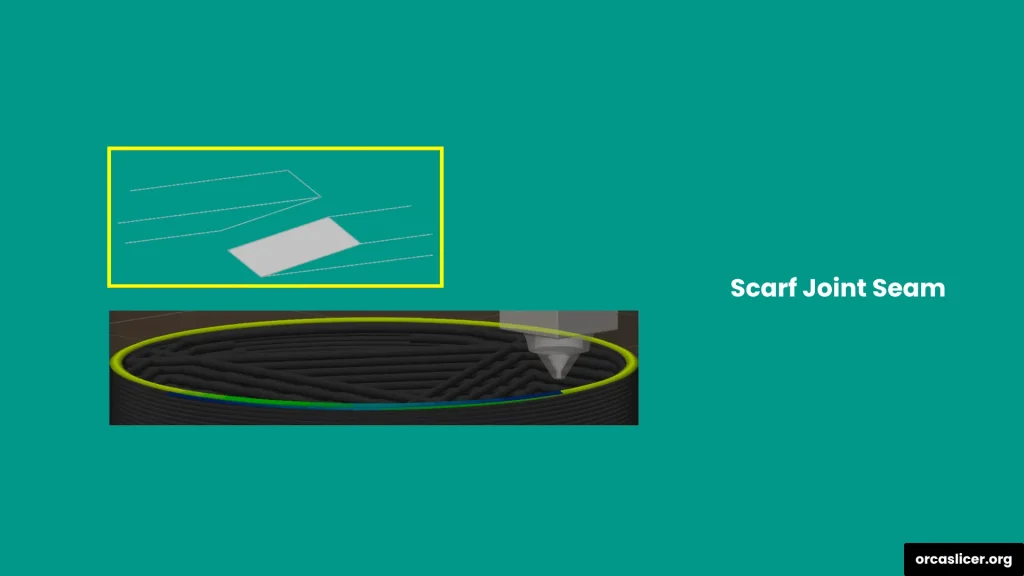
Scarf Joint Seam
The scarf joint seam technique overlaps two surfaces at an angle using a ramp-like connection, reducing seam visibility while strengthening the joint. This method softens transitions and maintains a smooth surface finish.

Advantages
- Minimizes visible z-seams on the model.
- Improves the appearance of curved surfaces.
- Increases part strength by overlapping seams instead of stacking them.
Disadvantages
- Slightly increases printing time.
- Less effective for sharp corners or steep overhangs.
- Requires careful tuning of speed, length, and flow rate for best results.
Scarf Joint Seam Types
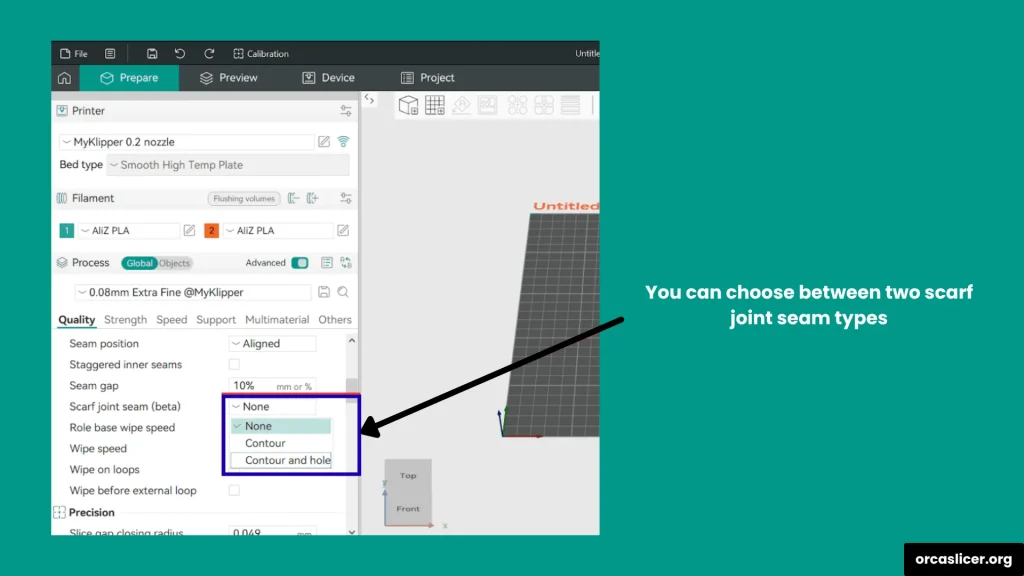
- Contour: Applied on curved outer surfaces, improving appearance and flow continuity.
- Contour and Hole: Applied on inner walls and curved perimeters around holes for better uniformity.
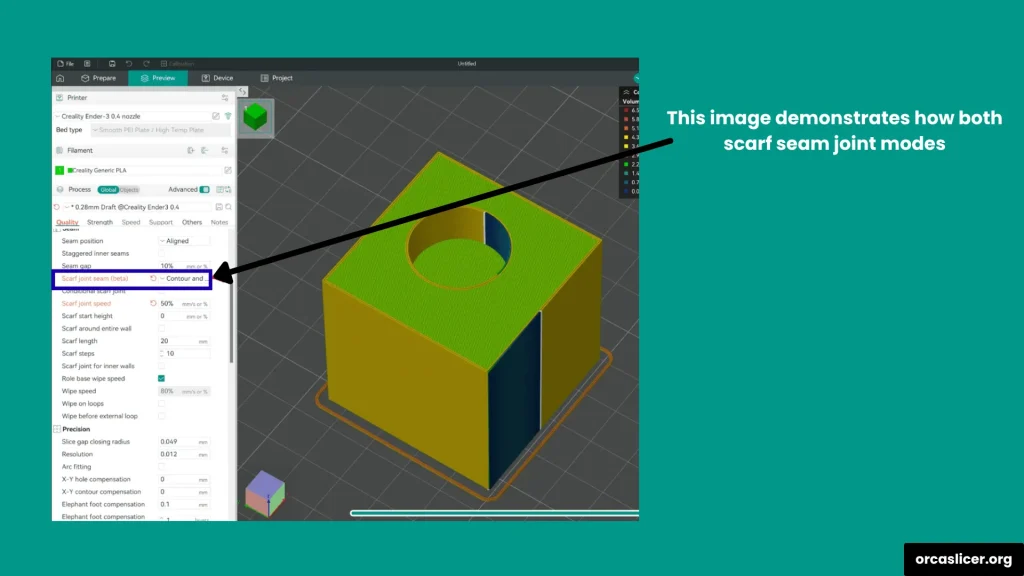
Conditional Scarf Joint
This setting automatically adjusts seam type based on the geometry of your model. It applies standard seam settings for straight or flat parts and switches to scarf joint seams for curved or contoured surfaces. This ensures both visual consistency and printing efficiency.
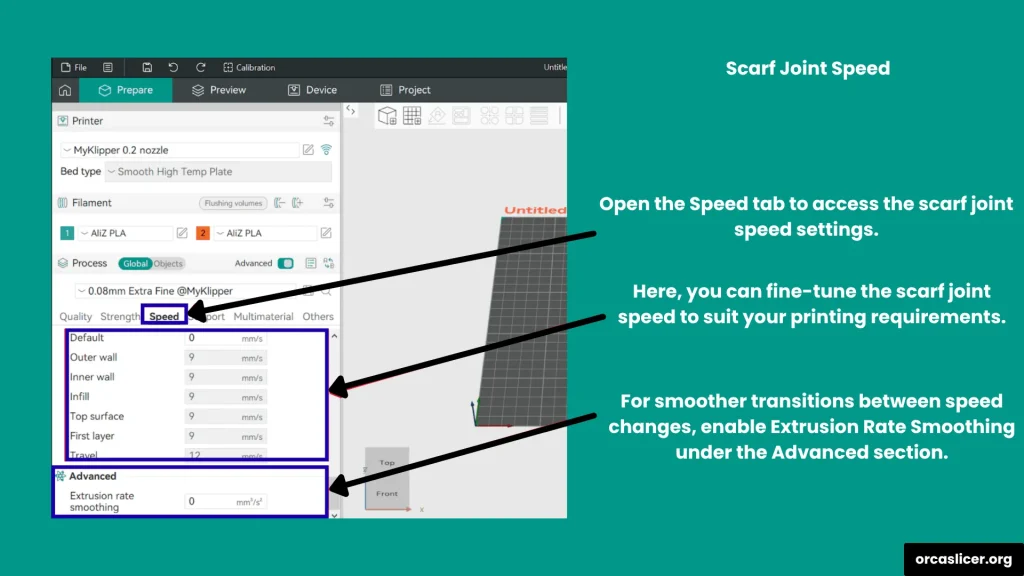
Scarf Joint Speed
It controls how fast scarf joints are printed.
- For best results, use lower speeds (below 100 mm/s).
- If inner and outer wall speeds differ, enable Extrusion Rate Smoothening to balance them.
- Setting the speed as a percentage of both wall speeds helps maintain smooth flow.
Recommended Default: 100% for balanced performance.
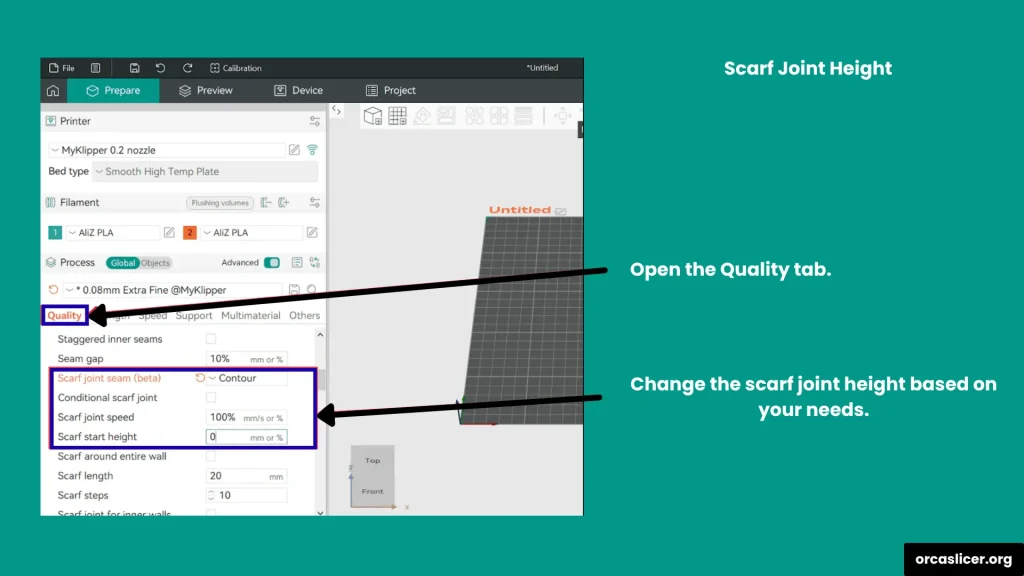
Scarf Joint Height
It defines the vertical offset where the scarf ramp begins. It can be set in millimeters or as a percentage of the current layer height.
- Set it slightly below the layer height for a smooth blend between layers.
- Example: For a 0.2 mm layer height, use 0.1 mm or 50% for best results.
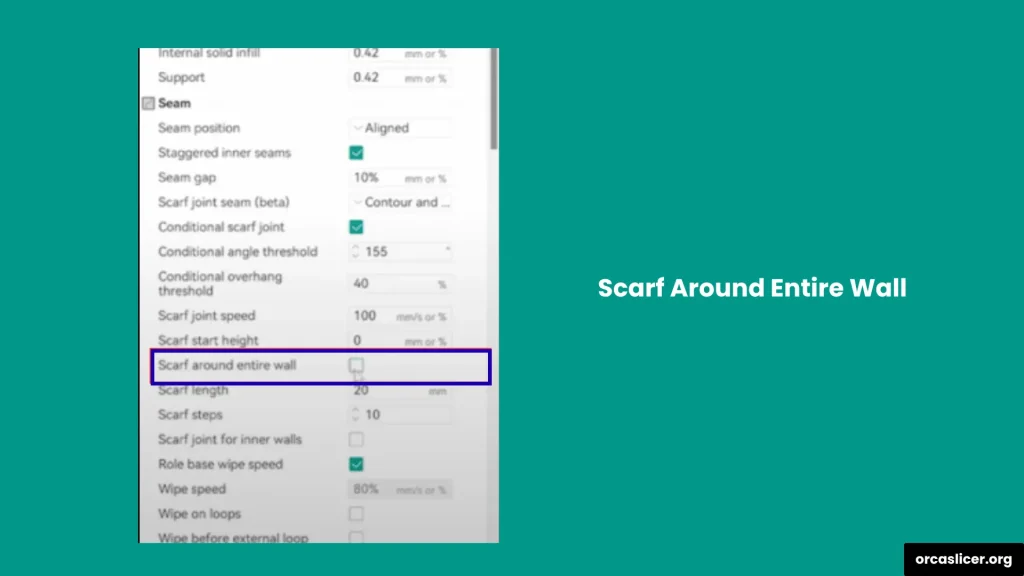
Scarf Around Entire Wall
This option prints the scarf joint around the entire wall perimeter. It is generally disabled by default because it increases print time without significantly improving seam quality.
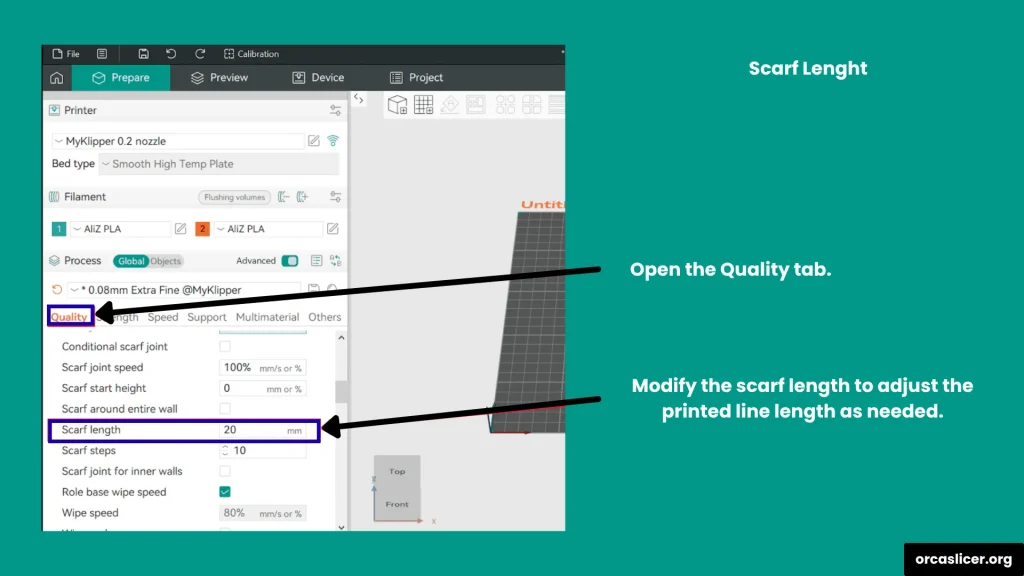
Scarf Length
It determines the horizontal distance of the scarf joint ramp. Adjusting this value lets you fine-tune the overlap transition for the best surface smoothness.
Scarf Steps
It specifies the number of segments used to create the scarf joint. A higher number means smoother transitions.
Recommended Default: 10 steps for optimal quality and performance.
Scarf Joint Flow Ratio
It controls the extrusion flow rate during scarf seam printing.
Recommended: Keep at 100% for balanced flow. Lower flow ratios may cause under-extrusion and visible surface gaps.
Scarf Joint for Inner Walls
This enables scarf joints on internal perimeters, such as holes or cavities, to make seams less visible and improve bonding strength inside the print.
Role-Based Wipe Speed
Enabling role-based wipe speed synchronizes the wipe speed with the printing speed of that section, ensuring consistent nozzle movement and better surface uniformity.
Wipe Speed
Wipe speed manages how quickly the nozzle moves while performing a cleaning motion before shifting to the next printing area. If role-based wipe speed is disabled, you can manually set the absolute wipe speed. Choose either a fixed speed or a percentage of your printer’s overall travel speed for full control.
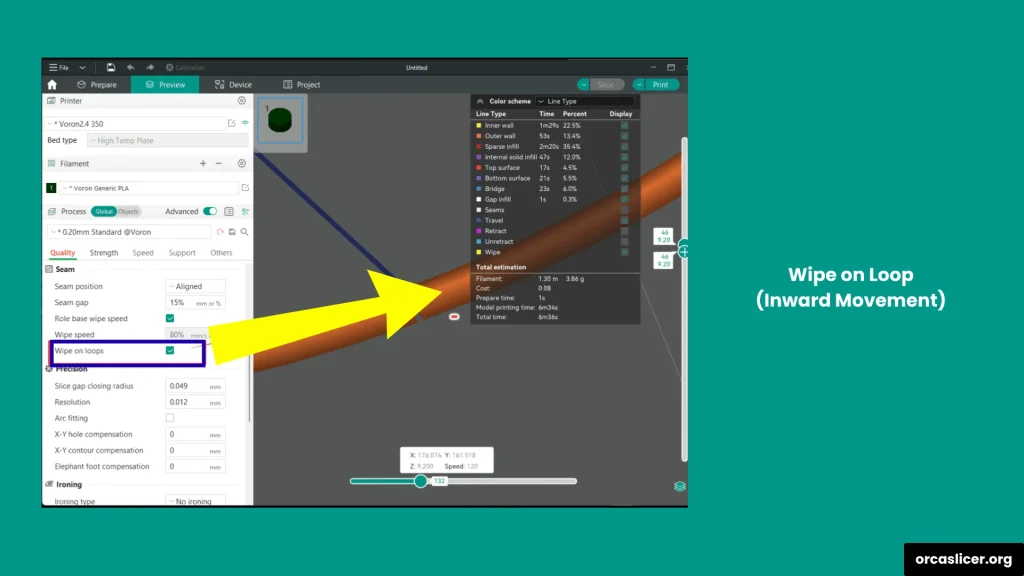
Wipe on Loop (Inward Movement)
When a loop (a complete print cycle) finishes, moving the nozzle slightly inward helps tuck the seam into the part, reducing uneven marks. This also helps clean the nozzle before printing the next area and decreases stringing.
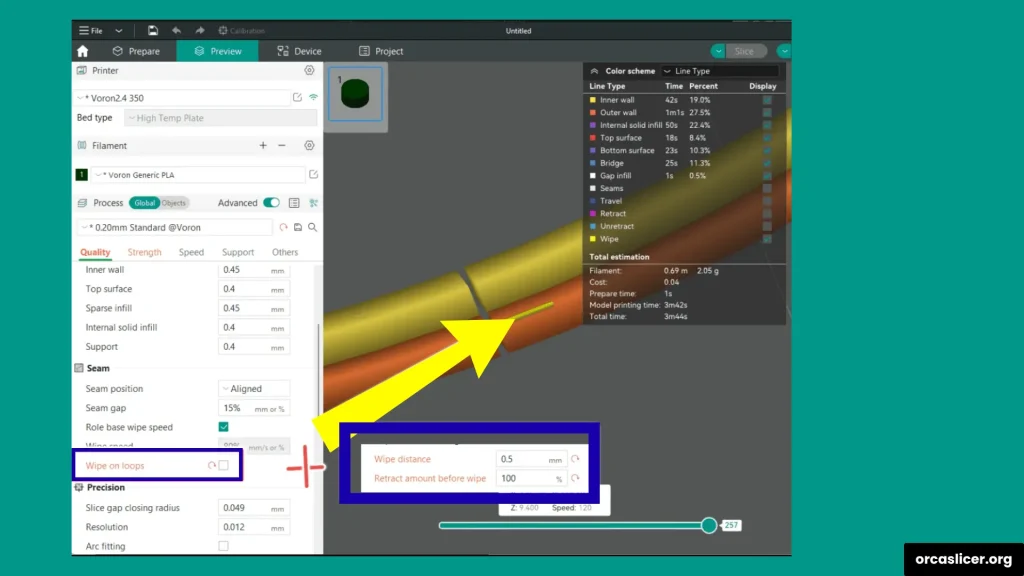
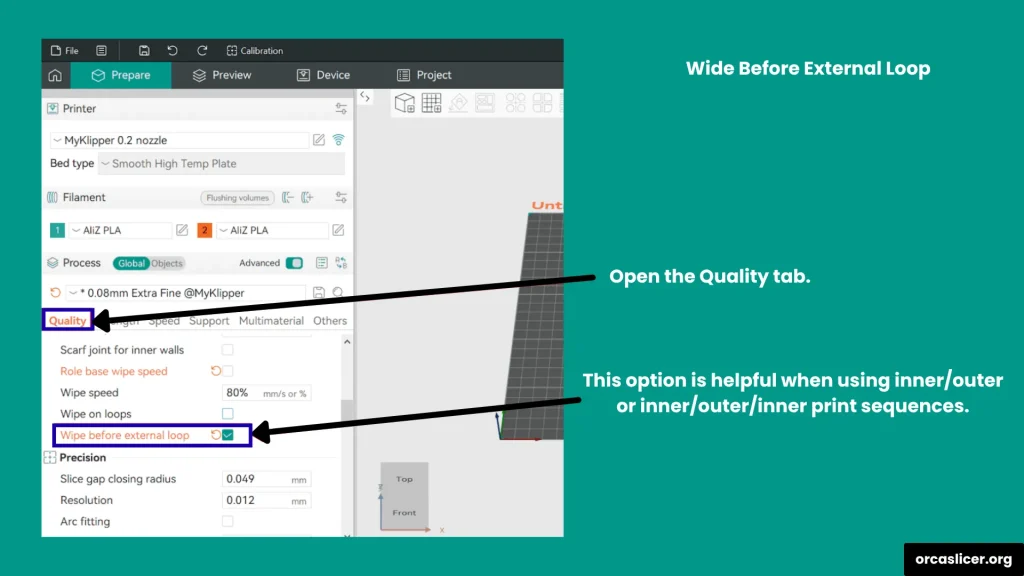
Wipe Before External Loop
This setting minimizes overextrusion marks by performing a retraction movement slightly inward before starting the external perimeter. It hides small extrusion defects inside the model, improving the outer surface quality. This is especially helpful when using inner/outer or inner/outer/inner wall print orders.
Tips for Better Seams in Orca Slicer
In FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) 3D printing, seams are unavoidable, but you can still control their visibility and quality with the right settings. Here are some pro tips to help you achieve cleaner, less noticeable seams and improve the overall finish of your prints.
Hide the Seam Whenever Possible
Try positioning the seam in less visible areas of your print. You can use settings like “Aligned Back” or “Back” to place the seam away from the front-facing side.
For smoother results, enable the Scarf Joint Seam technique. It overlaps the seam in an angled pattern, reducing its visibility and improving the aesthetic appearance of your model. This method works best for designs with minimal or no overhangs.
Keep the Seam Clean and Distinct
A clean seam looks far better than a messy one. To ensure this:
- Use the Seam Gap option to prevent bulging at the seam.
- Enable Role-Based Wipe Speed to make nozzle movement consistent with the print speed.
- Activate Wipe on Loop to tuck the seam inward and minimize unevenness.
- Turn on Wipe Before External Loop to hide any small extrusion marks inside the model.
These features help you maintain clean transitions, reduce stringing, and give your 3D prints a professional, polished finish.
Troubleshooting Seam Performance
Even with the best slicer settings, achieving perfect seams in FFF 3D printing can be tricky. A seam marks the start and end of each printed layer, and its quality depends on how well the printer manages extrusion, travel speed, and pressure control. By fine-tuning these factors, you can significantly improve seam consistency, strength, and appearance.
Below is a complete troubleshooting guide to help you fix seam issues in Orca Slicer for traditional (non-scarf) seams.

Key Factors That Affect Seam Quality
- Extrusion Rate: Seam performance is directly linked to the stability of the extrusion flow. A well-controlled extrusion prevents oozing and underextrusion, resulting in smooth seams.
- Layer Start and Stop Points: The printer should begin and end each layer at the same position for a uniform, consistent seam line.
In reality, FFF printers can’t always perform ideally due to mechanical tolerances, nozzle pressure variations, and material differences, but precise settings can help achieve near-perfect results.
Troubleshooting Tips for the Start of the Seam
There are generally two printing behaviors to consider:
- The toolhead prints a line, retracts, moves back, and starts printing again. This leads to more travel time and can cause blobs or gaps from filament oozing.
- The toolhead prints an internal perimeter, then moves slightly to print the outer perimeter without retracting. This produces cleaner seams and fewer artifacts.
To fix problems at the start of the seam, follow these steps:
Calibration and Settings
- Calibrate Pressure Advance (PA): Too little pressure advance causes excess nozzle pressure, leading to blobs. Too much PA can cause underextrusion. Tune this to balance both.
- Increase Travel Speed: Use the highest stable travel speed your printer supports. Faster travel reduces oozing by minimizing idle time at the nozzle.
- Enable Wipe Before External Perimeter: This helps the nozzle retract slightly inward before starting a new perimeter, hiding any overextrusion within the model.
- Optimize Travel Distance Threshold: Set the threshold high enough (typically 2–4 mm) so short movements don’t trigger unnecessary retraction/de-retraction cycles.
- Enable Retraction on Layer Change: Ensures the nozzle starts each layer with the filament retracted, maintaining consistent pressure.
Hardware-Related Seam Issues
Hardware also affects seam performance:
Nozzle Type:
- High-flow nozzles have large melt zones that cause poor extrusion control and higher stringing.
- Standard nozzles offer better precision and balance.
- CHT-type nozzles perform moderately well, while volcano nozzles tend to cause more oozing.
Nozzle Diameter:
- Smaller nozzles (e.g., 0.2–0.25 mm) provide better seam control and fine detail, while larger ones (e.g., 0.6 mm) may produce bulkier seams.
Troubleshooting the End of a Seam
The end of the seam is where extrusion stops, and managing pressure here is important.
Fixes and Adjustments
- Tune Pressure Advance (PA): If too low, the nozzle remains pressurized and causes bulging. If too high, you’ll see underextrusion and visible gaps at layer ends. Run a PA calibration test to find your optimal value for speed, acceleration, and material.
- Adjust Seam Gap: Keep a slightly larger seam gap to absorb small mechanical inaccuracies at the end of extrusion. This prevents visible blobs or stringing.
- Wiping Technique: Enable Wipe on Loop to create a consistent, tucked-in seam. This makes the seam cleaner, stronger, and visually even.
Pro Tip: Balance Speed and Pressure
Set your Pressure Advance first, then fix your travel speed, and finally fine-tune the seam gap to reach the ideal seam balance. This “plug-and-play” approach saves time and produces consistent, professional-quality results.
Wall Ordering’s Role in Seam Appearance
The order of perimeter printing affects seam visibility and surface smoothness:
- Long-distance travel before the outer perimeter: Causes stringing and small artifacts.
- Short-distance travel between inner and outer perimeters: Produces cleaner, tighter seams.
Recommended Print Order: Inner → Outer → Inner
This minimizes retractions, maintains consistent nozzle pressure, and gives smoother surface transitions compared to Outer → Inner order.
By following these troubleshooting methods, you can refine your seam control in Orca Slicer, achieving stronger, cleaner, and nearly invisible seams.