Auxiliary Fan Settings
Auxiliary fans are additional cooling fans placed near the printing chamber to help cool the extruded filament as it comes out of the nozzle. This quick cooling is essential for layer bonding, stability, and overall print quality.
If the auxiliary fan is not set up correctly, the filament may not harden fast enough, which can lead to imperfect layers, sagging, or surface defects. On the other hand, setting your auxiliary fan speed and timing to the right values ensures smooth surface finishes, zero material wastage, and no visible irregularities.
Configuring these settings directly in Orca Slicer allows you to maintain consistent cooling and achieve the high-quality results your 3D prints deserve.
How to Configure Auxiliary Fan Settings in Orca Slicer
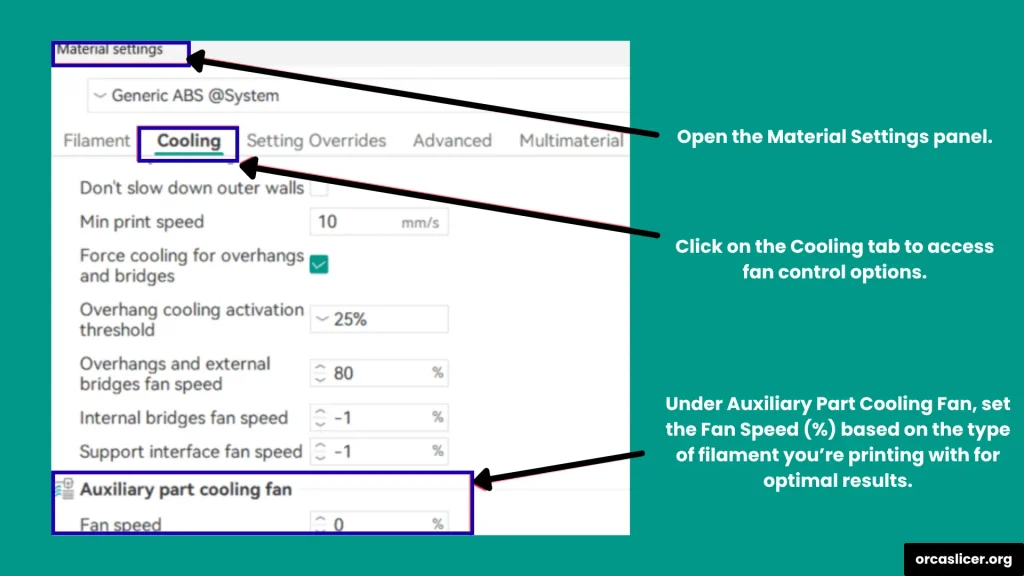
You can configure all fan-related settings directly in the Printer Settings tab of Orca Slicer. Follow these steps to adjust your Auxiliary Fan configuration:
- Open Orca Slicer and go to Printer Settings.
- Select Basic Information and then choose Auxiliary Fan under the cooling options.
- Once you enable the Auxiliary Fan setting, open Filament Settings.
- Go to the Cooling tab and set your fan speed percentage based on your filament material.
This setup allows you to control airflow efficiently, ensuring better print cooling and surface finish.

G-code Concept and the Keys for Settings
If you are using Klipper firmware, you can simplify these commands by creating Macros. Macros let you save your fan control settings and reuse them anytime you need to work with an auxiliary fan.
In Orca Slicer, you can use the commands M106 P# and M107 P# to manage any fan controlled by the slicer. Here’s what each command does:
- M106: Turns on the selected fan and sets its speed.
- M107: Turns off the specified fan.
Fan Parameter Keys
- P0: Controls the basic cooling fan for printed parts.
- P1: Manages any additional fan used during printing.
- P2: Controls Auxiliary, CPAP, or Booster fans.
- P3: Controls Exhaust or Enclosure fans.
These parameters help manage various fans and blowers that handle airflow and cooling performance during printing.
Even though these numeric codes can seem complicated, Klipper makes them easy to handle. You can create custom Macros to rename these numeric indexes with clear and memorable fan names. For example, instead of remembering P2, you can rename it as AUX_FAN in your macro file.
This mapping helps you connect the Orca Slicer’s numeric index to your physical fans for better control and quick access.
Simple Option (Indexes Only)
If you prefer not to use custom names, you can link the numeric indexes directly:
- fan0, fan2, fan3 : These represent different fan channels connected to your printer.
# Primary cooling unit
[fan_generic fan0]
pin: PA7
cycle_time: 0.01
hardware_pwm: false
# Secondary airflow fan (remove if your setup doesn’t include this)
[fan_generic fan2]
pin: PA8
cycle_time: 0.01
hardware_pwm: false
# Ventilation or chamber circulation fan (delete if not available)
[fan_generic fan3]
pin: PA9
cycle_time: 0.01
hardware_pwm: false
[gcode_macro M106]
gcode:
{% set fan = 'fan' + (params.P|int if params.P is defined else 0)|string %}
{% set speed = (params.S|float / 255 if params.S is defined else 1.0) %}
SET_FAN_SPEED FAN={fan} SPEED={speed}
[gcode_macro M107]
gcode:
{% set fan = 'fan' + (params.P|int if params.P is defined else 0)|string %}
{% if params.P is defined %}
SET_FAN_SPEED FAN={fan} SPEED=0
{% else %}
# When no P value is specified, disable all default cooling fans
SET_FAN_SPEED FAN=fan0 SPEED=0
SET_FAN_SPEED FAN=fan2 SPEED=0
SET_FAN_SPEED FAN=fan3 SPEED=0
{% endif %}Advanced Option (Index-to-Name Mapping)
In the advanced option, you can map descriptive names to each fan. Just make sure to keep the fan_map updated. This lets you reuse or repurpose fans without modifying Orca Slicer’s original output.
# Setup with clear fan names + notes matching OrcaSlicer order
[fan_generic CPAP] # blower 0 used by OrcaSlicer
pin: PB7
max_power: 0.8
shutdown_speed: 0
kick_start_time: 0.100
cycle_time: 0.005
hardware_pwm: False
off_below: 0.10
[fan_generic EXHAUST] # cooling unit 3 used by OrcaSlicer
pin: PE5
#limit_power:
#stop_speed:
cycle_time: 0.01
hardware_pwm: False
#boost_start_time:
off_below: 0.2
# If an extra one exists (for example P2), define here:
# [fan_generic AUX]
# pin: PXn
[gcode_macro M106]
description: "Adjust fan rotation (works with Orca)"
gcode:
{% set fan_map = {
0: "CPAP", # Orca P0 → CPAP airflow
3: "EXHAUST", # Orca P3 → Ventilation fan
# 2: "AUX", # Enable if AUX is declared
} %}
{% set p = params.P|int if 'P' in params else 0 %}
{% set fan = fan_map[p] if p in fan_map else fan_map[0] %}
{% set speed = (params.S|float / 255 if 'S' in params else 1.0) %}
SET_FAN_SPEED FAN={fan} SPEED={speed}
[gcode_macro M107]
description: "Disable fan activity. No P = all, P# = one target"
gcode:
{% set fan_map = {
0: "CPAP",
3: "EXHAUST",
# 2: "AUX",
} %}
{% if 'P' in params %}
{% set p = params.P|int %}
{% if p in fan_map %}
SET_FAN_SPEED FAN={fan_map[p]} SPEED=0
{% else %}
RESPOND PREFIX="warn" MSG="Unrecognized fan ID P{{p}}"
{% endif %}
{% else %}
# When no P is defined → shut down all connected fans
{% for f in fan_map.values() %}
SET_FAN_SPEED FAN={f} SPEED=0
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}Quick Customization Tips
- Add or remove keys or parameters from the fan_map to adjust your fan setup.
- You can modify properties like max_power, off_below, or cycle_time depending on your fan type.
Usage Examples
- From Orca Slicer: M106 P0 S255 (sets CPAP to 100%), M106 P3 S128 (sets Exhaust to about 50%).
- Turn off one fan: M107 P3.
- Turn off all fans: M107.
- To set speeds manually, use the Klipper console command: SET_FAN_SPEED FAN=CPAP SPEED=0.7.
Things to Remember
- In Klipper-based printers, Orca Slicer uses M106 with P2 to control the auxiliary fan.
- The S parameter defines fan speed, calibrated from 0–255, and represented as a percentage in Orca Slicer.
- Auxiliary fan settings can also be adjusted in Filament Settings, allowing material-specific configurations.
Once you finish configuring the primary and secondary fans, it’s essential to manage the temperature control carefully to maintain consistent print quality and airflow throughout the printing process.